Fig.3. Hsf1 KO mice with a prenatal history of challenge exposure show increased susceptibility to PTZ-induced seizures at the juvenile stage.
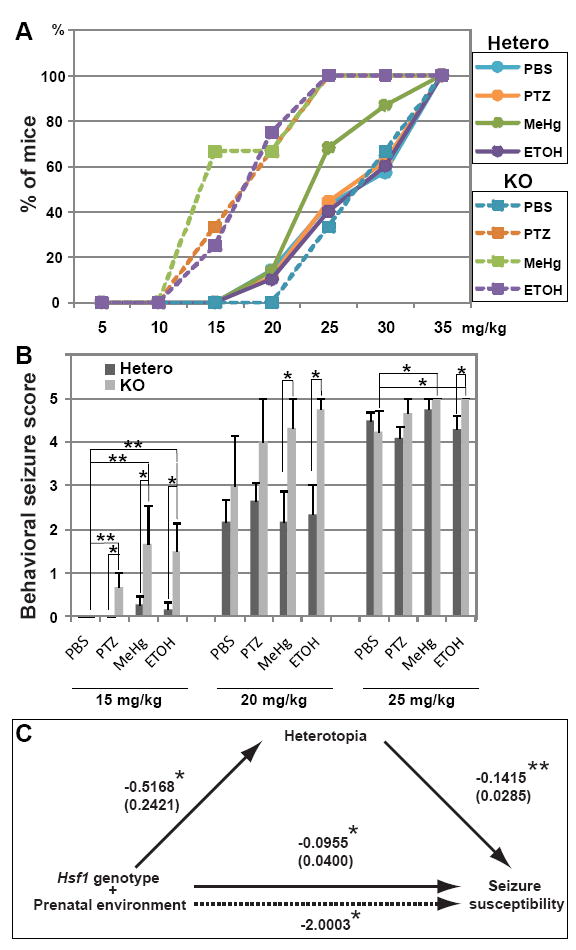
(A) Dose-response cumulative curves for induction of tonic-clonic seizures demonstrate greater PTZ sensitivity of Hsf1 KO mice prenatally exposed to challenges compared to heterozygous littermates and KO mice exposed to control treatment. p < 0.001 by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test between Hsf1 KO mice prenatally exposed to indicated substrates (except PBS) and heterozygotes with the same exposure or Hsf1 KO mice exposed to PBS. The comparison between heterozygotes prenatally exposed to challenges and those exposed to PBS shows no significant difference, except that a weak effect of MeHg is detected under our experimental condition (p = 0.0082 between MeHg- and PBS-exposed heterozygotes). n ≥ 4 offspring born from multiple dams for each experimental condition. (B) Seizure score values with increasing cumulative doses of PTZ. Hsf1 KO mice prenatally exposed to challenges showed significantly greater behavioral seizure score values at 15 to 25 mg/kg compared with their heterozygous littermates. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001 by the Mann-Whitney U test. n ≥ 4 offspring born from multiple dams for each experimental condition. (C) Mediational regression analysis of Hsf1 genotype, prenatal environment, heterotopia formation and seizure susceptibility. The values on continuous lines denote the standardized regression coefficient (Beta). Standard errors are indicated in parentheses. The value on a dotted line, which represents the path when heterotopia formation is treated as a mediator, is the Sobel statistic value that indicates the strength of the indirect effect. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.0001. Both the direct effect and indirect effect (through heterotopia formation) of both Hsf1 genotype and prenatal environment on seizure susceptibility are significant, indicating partial mediation of Hsf1 genotype and prenatal environment on seizure susceptibility.
