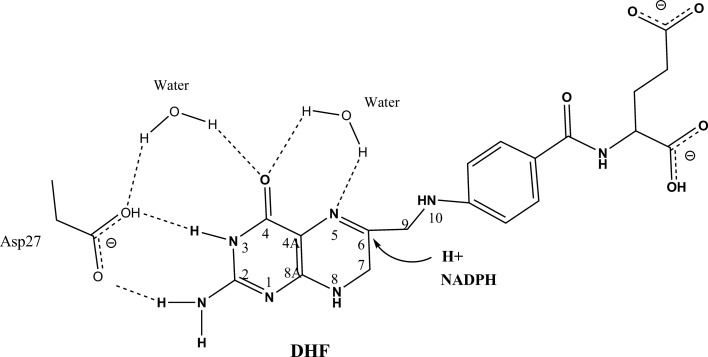
Figure 1.
A proposed mechanism of dihydrofolate (DHF) reduction. The N5 atom of folate might be directly protonated by a neighboring water molecule. Another proposed mechanism involves a proton relay from the catalytic Asp27 to a water molecule and the tautomerized O4 atom of DHF. Hydride transfer occurs from NADPH to the C6 of DHF to convert DHF to tetrahydrofolate (THF).