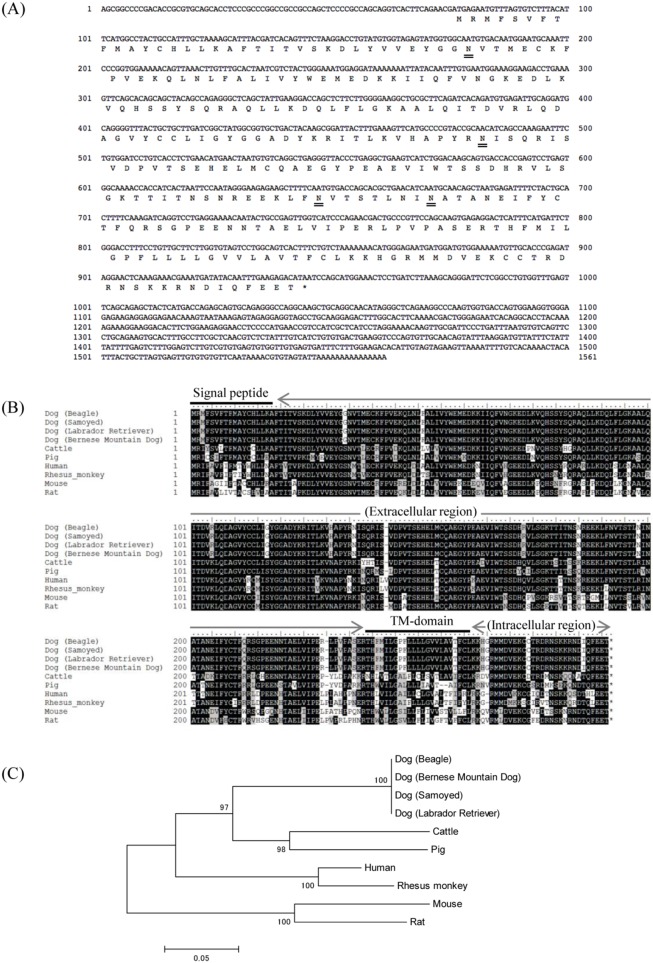
Figure 2. Sequence analysis of canine PD-L1.
(A) Nucleic acid and deduced amino acid sequences of canine PD-L1 cDNA. Canine PD-L1 cDNA encodes for a 289 amino acid polypeptide. Predicted N-glycosylation sites in the amino acid sequence of canine PD-L1 are doubly underlined. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of vertebrate PD-L1 amino acid sequences. Predicted domains and regions of canine PD-L1 are shown in the figure. Signal peptide, 1–18; transmembrane domain, 237–259. Canine PD-L1 consists of an extracellular region, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular region. (C) Phylogenetic tree of the canine PD-L1 sequence in relation to those of other vertebrate species. The bootstrap consensus tree was inferred from 1000 replicates (the numbers next to the branches indicate the bootstrap percentage). The scale indicates the divergence time.