Figure 3. Establishment of canine PD-1– or PD-L1– expressing cells and Ig fusion recombinant proteins.
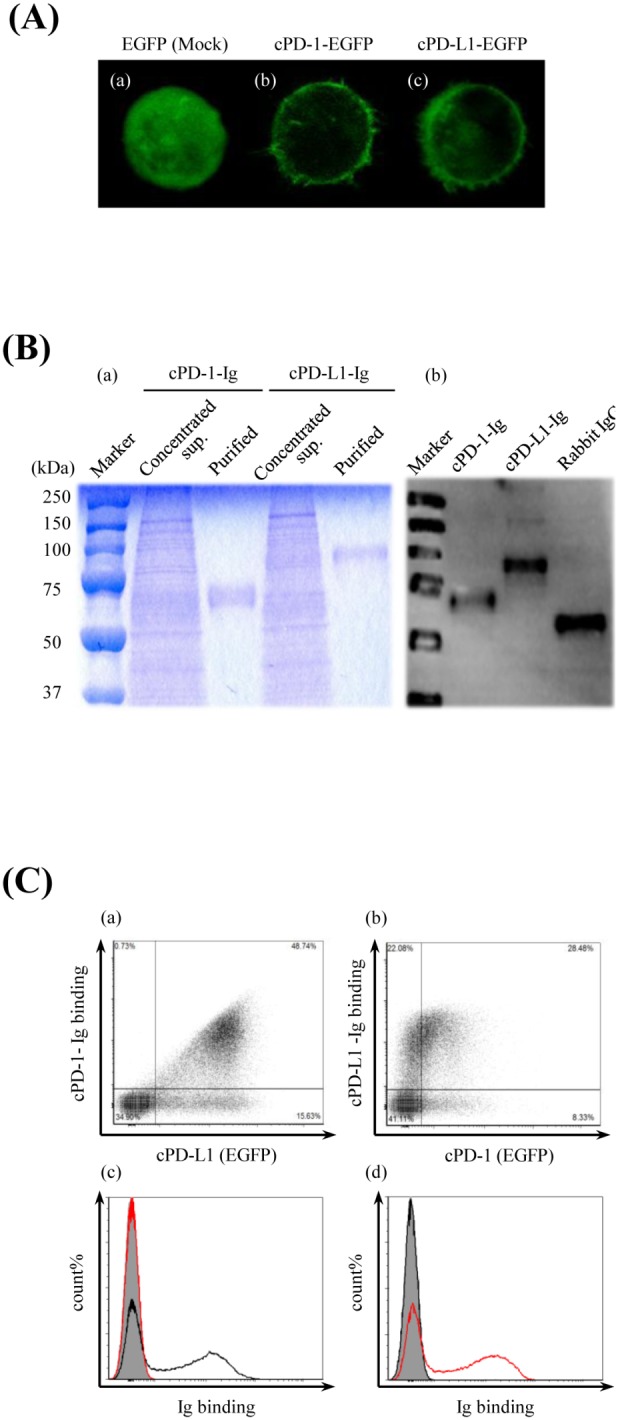
(A) Canine PD-1–EGFP– or canine PD-L1–EGFP–expressing cell. The subcellular distributions of EGFP only, cPD-1–EGFP, and cPD-L1–EGFP in transiently transfected Cos7 cells were analyzed by a confocal microscope (400×). Cos7 cells were transfected with (a) pEGFP-N2 vector only (Mock), (b) pEGFP-N2–cPD-1 or (c) pEGFP-N2–cPD-L1. (B) Production and purification of Ig fusion recombinant proteins. The canine PD-1 and canine PD-L1 extracellular regions combined to the rabbit IgG Fc region (cPD-1–Ig, cPD-L1–Ig) were expressed as soluble proteins in the culture supernatant by stably expressing CHO-DG44 cells, which had been transfected with pCXN2.1–rabbit IgG Fc-cPD-1 or pCXN2.1–rabbit IgG Fc-cPD-L1. (a) SDS–PAGE analysis of the concentrated culture supernatant of the expressing cells and the purified Ig fusion proteins. (b) Western blot analysis of the purified Ig fusion proteins. Rabbit IgG was used as a positive control. (C) Canine PD-L1 binds to canine PD-1. Transiently transfected cPD-1–EGFP– or cPD-L1–EGFP–expressing Cos7 cells were incubated with cPD-L1–Ig or cPD-1–Ig, respectively. The cells were washed and the binding of the Ig fusion proteins was analyzed by flow cytometry using a fluorescent labeled anti-rabbit IgG Fc antibody. cPD-1–EGFP or cPD-L1–EGFP expression on the transfected Cos7 cells were confirmed by EGFP fluorescence. (a) Binding of cPD-1–Ig to cPD-L1–expressing cells. (b) Binding of cPD-L1–Ig to cPD-1–expressing cells. (c) Histogram analysis of cPD-1–Ig binding to cPD-L1–EGFP–expressing cells. Black line, cPD-1–Ig; red line, cPD-L1–Ig; shaded area, rabbit IgG. (d) Histogram analysis of cPD-L1–Ig binding to cPD-1–EGFP–expressing cells. Black line, cPD-1–Ig; red line, cPD-L1–Ig; shaded area, rabbit IgG.
