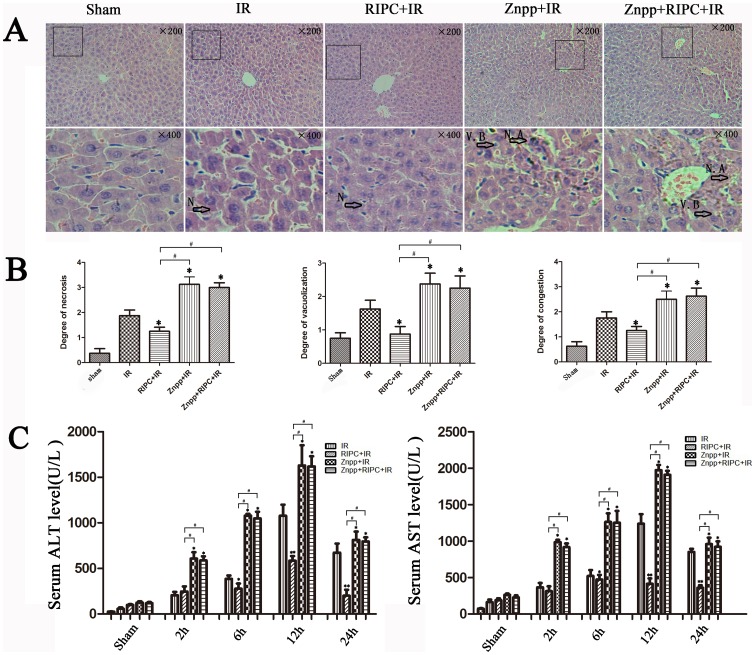
Figure 3. Increased HO-1 and autophagy alleviated liver damage.
(A) IR treatment increases the histopathologic changes of liver. Extensive areas of hepatocyte necrosis (N), vacuolation (V) and sinusoidal congestion were observed in the IR group. The Znpp+IR and Znpp+RIPC+IR group showed markedly higher hepatocyte necrosis accumulation (N. A) and vacuo(V), whereas the RIPC+IR group still showed large areas of normal liver architecture, similar to the sham group mice (original magnification 200×; insets 400×). (B) The mean injury score of the RIPC+IR group was significantly lower than the IR group according to Suzuki's histologic classification. The mean injury scores in the Znpp+IR and Znpp+RIPC+IR groups were significantly higher than in the IR and RIPC+IR groups (*P<0.05 compared with the IR group; #P<0.05 compared with the RIPC+IR group). (C) IR treatment increased serum aminotransferase levels in mice compared with controls. Compared with the IR group, serum aminotransferase levels were lower in the RIPC+IR group. The mean serum levels of ALT and AST were highest in the Znpp+IR and Znpp+RIPC+IR groups. There were no significant differences in aminotransferase levels in the Znpp+IR and Znpp+RIPC+IR groups (*P<0.05 compared with the IR group; #P<0.05 compared with the RIPC+IR group).