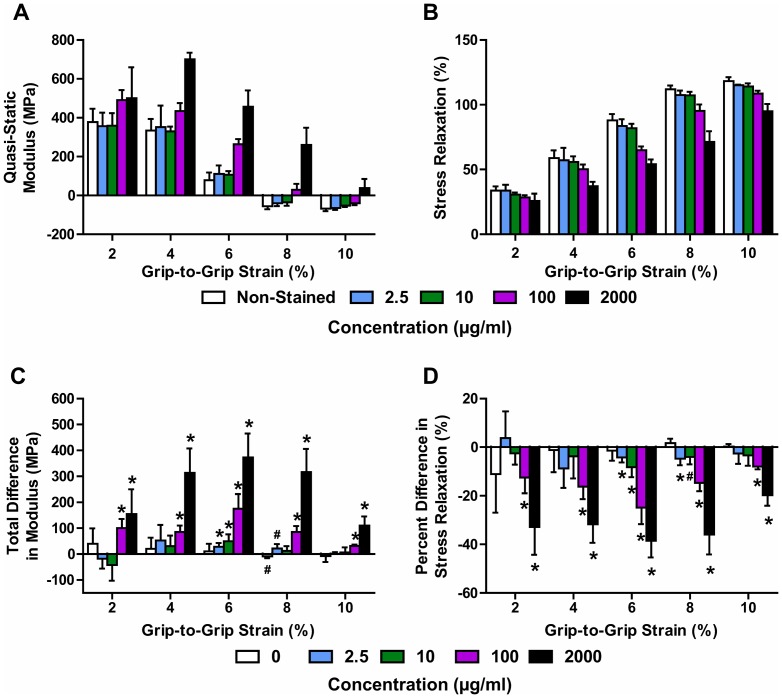
Figure 4. Macroscale mechanical properties as a function of DTAF concentration and applied grip-to-grip strain level.
(A) Samples stained at high concentrations (>10 µg/ml) maintain large positive quasi-static moduli at greater applied grip-to-grip strains, suggesting that DTAF increases the tissue yield strain. (B) Staining also reduced the amount of stress relaxation throughout testing, with greater effects observed with increasing DTAF concentration. Note: The Non-Stained group contains all the paired non-stained control samples (n = 16). (C,D) Paired differences between stained samples and non-stained controls confirm that high DTAF concentrations produce (C) large increases in quasi-static modulus and (D) decreases in stress relaxation at all applied grip-to-grip strain levels. Lower DTAF concentrations (≤10 µg/ml) exhibited relatively small effects at 6-8% grip-to-grip stains. *p<0.05, #p<0.10.