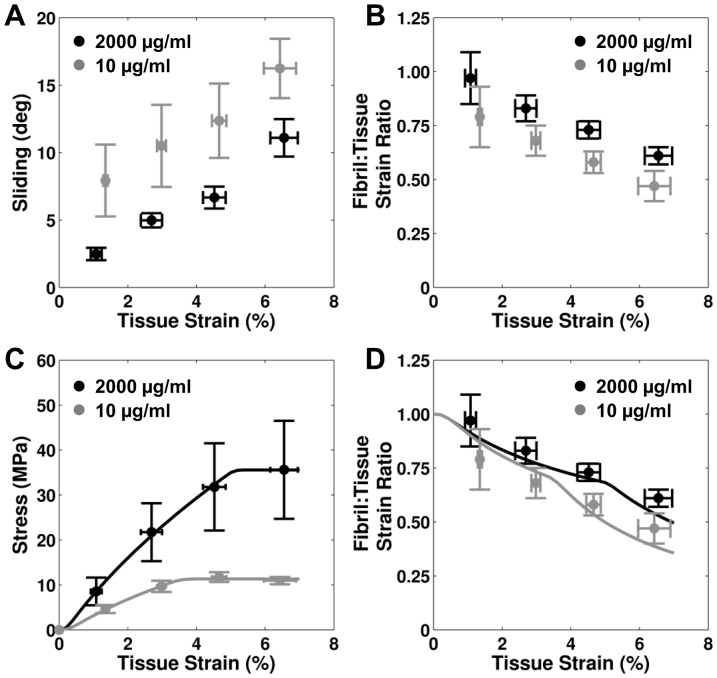
Figure 5. Results of multiscale testing and modeling.
Multiscale testing demonstrates that higher concentrations of DTAF (A) decrease interfibrillar sliding and (B) increase fibril strains. However, the relationship between both of these microscale deformations and the macroscale tissue strains are similar between the two DTAF concentrations. Additionally, a shear lag model incorporating a perfectly plastic interfibrillar shear stress was successful in (C) fitting the macroscale fascicle mechanics (R2 = 0.997) and (D) predicting the microscale fibril strains (R2 = 0.68) of tendon fascicles stained at 10 µg/ml. These results are similar to the model performance for samples stained at 2000 µg/ml [22]. Therefore, these data suggest that while DTAF alters fascicle multiscale mechanics it doesn' change the physical mechanisms underlying fascicle behavior.