Fig. 2.
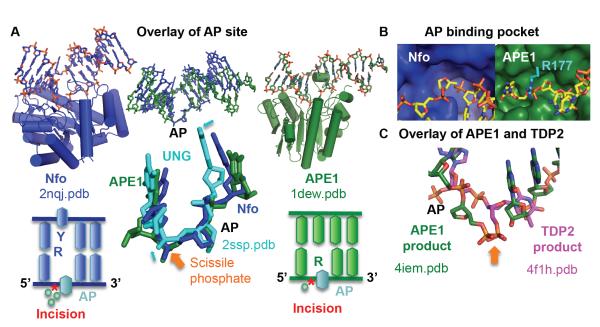
Nfo and APE1 share a common DNA sculpting to select for AP sites. A) Overlay of the AP site in substrate structures highlights the common DNA structure, despite the differences in protein structure and catalytic metals. The closeup highlights that this is not a default flipped out AP nucleotide conformation, as the abasic site in UNG shows small but significant shifts in phosphate and sugar positions (cyan arrows). Below each enzyme, a DNA schematic shows nucleotide flip and incision position (*). B) The shallow binding pocket (protein shown as a surface) selects for abasic sites. For clarity, Arg177 was shown in cyan. C) After overlay of the protein in APE1 and TDP2 DNA-bound structures, the scissile phosphate (orange arrow) matches, but the nucleotide is oriented inversely.