Abstract
AIM: To investigate the benefits of hyoscine butylbromide in polyp detection during colonoscopy by a meta-analysis of available randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
METHODS: Databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and the Science Citation Index up to September 2013, were searched. The primary outcome was polyp detection rate, and the secondary outcome was adenoma detection rate. The meta-analysis was performed using the free software Review Manager. Differences observed between the treated and the control groups were expressed as odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). A fixed-effects model was used to pool data when statistical heterogeneity was absent. If statistical heterogeneity was present (P < 0.05), a random-effects model was used.
RESULTS: The initial search identified nine articles. After screening, five RCTs with a total of 1998 patients were included in this meta-analysis. Of the five studies, all described a comparison of baseline patient characteristics and showed that there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups. Among the 1998 patients, 1006 received hyoscine butylbromide and 992 were allocated to the control group, and the polyp detection rate was reported. There were no significant differences between the treated and the control group (OR = 1.09, 95%CI: 0.91-1.31, P = 0.33). Four RCTs included 1882 patients, of whom 948 received hyoscine butylbromide, and the adenoma detection rate was reported. There were no significant differences between the treated and the control group (OR = 1.13, 95%CI: 0.92-1.38, P = 0.24).
CONCLUSION: The use of hyoscine butylbromide did not significantly improve the polyp detection rate during colonoscopy.
Keywords: Hyoscine butylbromide, Polyp detection, Adenoma detection, Colonoscopy
Core tip: There is a debate as to whether hyoscine butylbromide can really improve polyp detection during colonoscopy. We performed a meta-analysis of the results of randomized controlled trials to investigate the benefits of hyoscine butylbromide in polyp detection during colonoscopy. We found that the use of hyoscine butylbromide did not significantly improve the polyp detection rate during colonoscopy.
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common gastrointestinal cancers in the Asian-Pacific region due to socioeconomic development and adaptation of Western lifestyle[1]. Adenomatous polyps are usually the precursor of CRC, and early identification and removal prevent progression of colonic neoplasia[2]. Colonoscopy is currently the gold standard for the diagnosis of mucosal diseases[3]. However, polyps can remain undetected during colonoscopy, with a reported miss rate of 5%-32%[4], probably because some lesions lie in areas of the colonic surface that do not enter the field of view[5]. Therefore, improvements in polyp detection are a major focus of endoscopic research and quality improvement programs worldwide. The use of antispasmodic agents in colonoscopy is considered when the rationale is to reduce colonic spasm, which can impede advancement of the colonoscope and impair visualization of the mucosa[6]. The advantages of these agents have been proved in some trials with respect to speed and ease of colonoscope insertion[7] and ileal intubation rates[8,9]. In recent years, authors such as Corte et al[10] found that antispasmodic agents could reduce the depth of the haustral folds and may facilitate the detection of polyps. Hyoscine butylbromide, a well-known antispasmodic drug, can block muscarinic receptors and thus exert a parasympathicolytic action which results in a reduction in the tone and motility of smooth muscle[11,12]. This helps to achieve rapid spasmolysis, and may increase mucosal view and polyp detection[13]. Although adverse effects, such as visual accommodation disturbance, mild tachycardia, or a dry mouth have been observed, hyoscine butylbromide is still a well tolerated and safe drug, especially when monitored[11,14].
However, an ongoing debate still exists as to whether hyoscine butylbromide can really improve polyp detection during colonoscopy[15,16]. To critically appraise the current evidence, we performed a meta-analysis of the results of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to investigate the benefits of hyoscine butylbromide in polyp detection during colonoscopy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
Electronic databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and the Science Citation Index up to September 2013, were searched. Literature references were hand-searched during the same time period. The search terms used were “hyoscine butylbromide or buscopan and polyp detection”.
Study selection
The initial inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) RCTs regardless of whether they were single blinded, double blinded or unblinded; (2) the treatment group received hyoscine butylbromide during colonoscopy; and (3) a parallel control group received placebo during colonoscopy. Studies that met the initial inclusion criteria were further examined. Those with duplicate publications, unbalanced matching procedures or incomplete data were excluded. When publication duplication occurred, or the studies were reported in conference proceedings, the earliest publications were excluded.
Data extraction
Data were extracted independently by two reviewers (Cui PJ and Yao J) according to the prescribed selection criteria. Any disagreements were resolved by discussion between the two reviewers. The following data were extracted: the baseline trial data (e.g., mean age, gender, bowel preparation type, colonoscopy staff arrangement, methods of sedation during colonoscopy, and dosage and administration routes of hyoscine butylbromide); the outcomes of colonoscopy (polyp and adenoma detection rate, number of adenomas and polyps detected per patient). Where necessary, the corresponding authors were contacted to obtain supplementary information. The polyp/adenoma detection rate was defined as the number of patients with ≥ 1 polyp/adenoma divided by the total number of screened patients.
Study quality
The quality of the included trials was assessed using the Jadad composite scale[17] in addition to a description of an adequate method for allocation concealment. The Jadad score assesses descriptions of randomization, double blinding, and withdrawals or dropouts. It ranges from 0-5 points, with a low-quality study having a score of ≤ 2 and a high-quality study having a score of ≥ 3[18]. Study quality was assessed independently by two authors (Cui PJ and Yao J), and any discrepancies in interpretation were resolved by consensus (Table 1).
Table 1.
Quality analysis of included trials
| Study | Randomization method | Allocation concealment | Blinding | Withdrawals | Jadad score |
| Byun et al[20] | Not mentioned | Unclear | Double-blind | Not mentioned | 3 |
| Lee et al[21] | Computer-generated | Adequate | Double-blind | Not mentioned | 6 |
| Corte et al[10] | Computer-generated | Adequate | Double-blind | Described | 7 |
| de Brouwer et al[15] | Not mentioned | Unclear | Double-blind | Described | 4 |
| Rondonotti et al[16] | Computer-generated | Adequate | Double-blind | Described | 7 |
Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was performed using the free software Review Manager (Version 4.2.10, Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). Differences observed between the two groups were expressed as the odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). A fixed effects model was used to pool data when statistical heterogeneity was absent. If statistical heterogeneity was present (P < 0.05), a random effects model was used.
RESULTS
The initial search identified nine articles (Figure 1). After screening, six RCTs were identified. One study[19] compared outcomes unrelated to this meta-analysis, and was consequently excluded from the pooled meta-analysis. Therefore, five RCTs[10,15,16,20,21] were included in this meta-analysis. All five studies described a comparison of baseline patient characteristics and showed that there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. The principal characteristics of the included studies are shown in Tables 2 and 3. The outcomes were measured as follows.
Figure 1.
Search protocol for the meta-analysis.
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of included trials in the meta-analysis
| Study | Group | Age | Gender | Intervention | Time of intervention | Bowel preparation | Colonoscopy staff | Sedation |
| (M/F) | ||||||||
| Byun et al[20] | Hyoscine butylbromide | Not mentioned | 103 (total number) | 20 mg, iv | At the time of colonoscopic withdrawal | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Placebo | 102 (total number) | 1 mL NS, iv | ||||||
| Lee et al[21] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 59.4 ± 8.5 | 27/31 | 20 mg, iv | When the scope reached the cecum | Polyethylene glycol solution | A single experienced endoscopist | Midazolam, 3-5 mg, iv |
| Placebo | 58.4 ± 7.9 | 23/35 | 1 mL NS, iv | |||||
| Corte et al[10] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 60.6 ± 11.2 | 162/141 | 20 mg, iv | After the cecum was reached | PrepKit C; picoPrep; moviPrep; glycoPrep | 8 endoscopists, 14 fellows | Midazolam, fentanyl with or without propofol, iv |
| Placebo | 61.4 ± 10.4 | 157/141 | 1 mL NS, iv | |||||
| de Brouwer et al[15] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 61.5 | 156/184 | 20 mg, iv | When the cecum was reached and the withdrawal of the colonoscope was started | Polyethylene glycol solution | 5 gastroenterologists and 3 nurse endoscopists | Not mentioned |
| Placebo | 61.4 | 176/158 | 1 mL NS, iv | |||||
| Rondonotti et al[16] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 57.3 ± 11.5 | 90/112 | 20 mg, iv | At cecal intubation | Senna-based preparation | Six board-certified gastroenterologists | Midazolam and pethidine, iv |
| Placebo | 57.3 ± 13.5 | 87/113 | 1 mL NS, iv |
Table 3.
Characteristics of randomized comparisons of hyoscine butylbromide and placebo groups reported in the literature
| Study | Group | Polyp detection rate | Adenoma detection rate | Polyps per patient (n) | Adenomas per patient (n) |
| Byun et al[20] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 45.6% | 35.0% | NR | NR |
| Placebo | 39.2% | 29.4% | |||
| Lee et al[21] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 34.5% | NR | 0.9 ± 1.8 | NR |
| Placebo | 25.9% | 0.6 ± 1.2 | |||
| Corte et al[10] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 43.6% | 27.1% | 0.91 ± 0.084 | 0.55 ± 0.073 |
| Placebo | 36.6% | 21.8% | 0.70 ± 0.075 | 0.42 ± 0.062 | |
| de Brouwer et al[15] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 55.9% | 29.7% | 1.13 | NR |
| Placebo | 60.2% | 31.4% | 1.21 | ||
| Rondonotti et al[16] | Hyoscine butylbromide | 38.6% | 31.7% | NR | NR |
| Placebo | 37.0% | 28% |
NR: Not reported.
Primary outcome
In this report, we considered polyp detection rate as the primary outcome. All five studies[10,15,16,20,21] reported polyp detection rate. These trials included 1998 patients, of whom 1006 received hyoscine butylbromide and 992 were allocated to the control group. A total of 906 patients were found to have polyps on colonoscopy, including 467 patients (46.4%) in the hyoscine butylbromide group and 439 patients (44.3%) in the control group. There was no significant difference between the two groups (OR = 1.09, 95%CI: 0.91-1.31, P = 0.33) (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
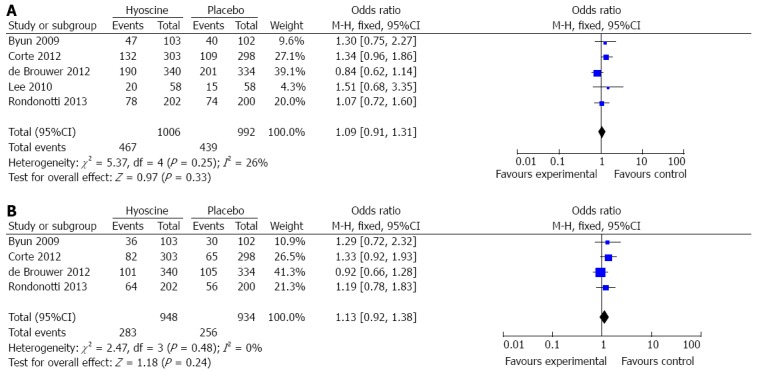
Comparison of polyp detection rate between the hyoscine butylbromide and placebo groups. A: Polyp detection rate; B: Adenoma detection rate.
Secondary outcome
The secondary outcome in this analysis was adenoma detection rate. The data were derived from four RCTs[10,15,16,20]. These trials included 1882 patients, 948 of whom received hyoscine butylbromide. A total of 539 patients were found to have adenomas on colonoscopy, including 283 patients (29.9%) in the hyoscine butylbromide group and 256 patients (27.4%) in the control group. There was no significant difference between the two groups (OR = 1.13, 95%CI: 0.92-1.38, P = 0.24) (Figure 2B).
DISCUSSION
The prevalence of polyps in the colon and rectum is high, as is the incidence of colorectal cancer[22]. Many individuals with polyps have been identified in recent years as a result of screening using colonoscopy[23]. Polyps are considered to be the precursor lesions of colorectal carcinoma, and colonoscopy which is used to identify and remove polyps has become standard practice for the prevention of CRC[24]. However, colonoscopy is not an ideal procedure in every case. Several reports have been published detailing the pitfalls of colonoscopy, which has significant miss rates for polyp and cancer detection[25,26]. Many factors including quality and timing of bowel preparation[27,28], colonoscopic technique[29], polyp position[30] and colonic contractility[13] may impede polyp detection. Several methods, including the administration of antispasmodic agents during colonoscopy to enhance the quality of colonoscopic examinations and to increase polyp detection rate, have been suggested. Colonic spasm can make it difficult for the endoscopist to advance the colonoscope and visualize the mucosa[6]. It seems that adequate colonic distension to improve mucosal view can lead to increased polyp and adenoma detection[31]. However, trials employing dicyclomine hydrochloride[32], glucagon[33], and atropine[34] have failed to show any benefit. Furthermore, there are some endoscopists who believe that the use of an antispasmodic may actually make colonoscopy more difficult by reducing colonic muscular tone[25]. In contrast to earlier studies, Lee et al[21] suggested that polyp detection may be enhanced by spasmolysis in patients with more pronounced colonic spasms. Corte et al[10] also found that antispasmodic agents could reduce the depth of the haustral folds and may facilitate the detection of polyps.
Hyoscine butylbromide, an antimuscarinic anticholinergic antispasmodic with a quaternary ammonium structure, is a commonly used, inexpensive, and safe drug. Its parasympathicolytic action results in a reduction in the tone and motility of smooth muscle[11,12]. These characteristics make it an attractive choice for the pretreatment of patients who undergo colonoscopy in an effort to obtain adequate colonic distension. The advantage of hyoscine butylbromide in facilitating ileal intubation was shown by Misra et al[9]. However, its advantage in increasing polyp detection is still debatable.
In the present meta-analysis, the baseline characteristics in the two groups were similar in all the studies. Hyoscine butylbromide 20 mg was administered intravenously after intubation of the cecum, thereby maximizing homogeneity for possible polyp detection. All five RCTs[10,15,16,20,21] evaluated the effectiveness of hyoscine butylbromide in improving polyp detection during colonoscopy. The meta-analysis showed that the polyp detection rate (OR = 1.09, 95%CI: 0.91-1.31, P = 0.33) was not correlated with the use of hyoscine butylbromide. The results of this meta-analysis indicated that hyoscine butylbromide did not improve the rate of polyp detection during colonoscopy. Moreover, there was no association between the use of hyoscine butylbromide and improvement in the detection of adenomas (OR = 1.13, 95%CI: 0.92-1.38, P = 0.24), although adenomas were not reported in all studies. We also evaluated the quality of these RCTs according to the Jadad score[17] and found that the results of the meta-analysis were consistent with the sensitivity analysis. Thus, the results showing the ineffectiveness of hyoscine butylbromide in improving the polyp detection rate during colonoscopy are credible and robust.
This meta-analysis had several limitations. The small number of studies and the restricted sample size in most trials implied that the quantitative analysis was not very powerful. Moreover, the experience of the endoscopist and the type of bowel preparation used may influence the results of colonoscopy[35]. In our meta-analysis, most trials involved different colonoscopy staff and there was no standardization of bowel preparation type, and this may account for the heterogeneity and influence our results. Further large multicenter studies based on a unified colonoscopy procedure are required.
In conclusion, the present meta-analysis showed that the use of hyoscine butylbromide did not improve the polyp detection rate during colonoscopy. Therefore, this analysis does not support the routine use of hyoscine butylbromide to improve the rate of polyp detection.
COMMENTS
Background
Some clinical trials have shown that hyoscine butylbromide increases mucosal view and polyp detection due to spasmolysis. However, there is an ongoing debate as to whether hyoscine butylbromide can really improve polyp detection during colonoscopy.
Research frontiers
Adenomatous polyps are usually the precursor of colorectal cancer, therefore, early identification and removal of polyps prevent progression of colonic neoplasia. Colonoscopy is currently the gold standard for the diagnosis of mucosal diseases. However, polyps can remain undetected during colonoscopy, with reported miss rates of 5%-32%. Therefore, improvements in polyp detection are a major focus of endoscopic research and quality improvement programs across the globe.
Innovations and breakthroughs
Meta-analyses of clinical trials have shown that there is no statistically significant benefit in the use of hyoscine butylbromide to improve the polyp detection rate during colonoscopy.
Applications
The present meta-analysis does not support the routine use of hyoscine butylbromide to improve the rate of polyp detection.
Terminology
Hyoscine butylbromide, an antispasmodic drug, can block muscarinic receptors and thus exert a parasympathicolytic action which results in a reduction in the tone and motility of smooth muscle.
Peer review
In this article, the authors investigated the benefits of hyoscine butylbromide in polyp detection during colonoscopy by a meta-analysis of available randomized controlled trials. The results gave no support to the routine use of hyoscine butylbromide as a tool to improve the rate of polyp detection.
Footnotes
P- Reviewers: Kopacova M, Lassandro F, Misra SP, Nash GF, Oka SM, Seow-Choe F S- Editor: Gou SX L- Editor: Wang TQ E- Editor: Liu XM
References
- 1.Yang J, Peng JY, Chen W. Synchronous colorectal cancers: a review of clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Dig Surg. 2011;28:379–385. doi: 10.1159/000334073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Muto T, Bussey HJ, Morson BC. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975;36:2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Winawer S, Fletcher R, Rex D, Bond J, Burt R, Ferrucci J, Ganiats T, Levin T, Woolf S, Johnson D, et al. Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: clinical guidelines and rationale-Update based on new evidence. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:544–560. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Rijn JC, Reitsma JB, Stoker J, Bossuyt PM, van Deventer SJ, Dekker E. Polyp miss rate determined by tandem colonoscopy: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rex DK. Accessing proximal aspects of folds and flexures during colonoscopy: impact of a pediatric colonoscope with a short bending section. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1504–1507. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marshall JB, Patel M, Mahajan RJ, Early DS, King PD, Banerjee B. Benefit of intravenous antispasmodic (hyoscyamine sulfate) as premedication for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:720–726. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chaptini LA, Janec EM, Seltzer G, Peikin S, Elfant AB. Sublingual hyoscyamine spray as premedication for colonoscopy: a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Am J Surg. 2008;196:51–55. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ansari A, Soon SY, Saunders BP, Sanderson JD. A prospective study of the technical feasibility of ileoscopy at colonoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:1184–1186. doi: 10.1080/00365520310006018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Misra SP, Dwivedi M. Role of intravenously administered hyoscine butyl bromide in retrograde terminal ileoscopy: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:1820–1823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i12.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Corte C, Dahlenburg L, Selby W, Griffin S, Byrne C, Chua T, Kaffes A. Hyoscine butylbromide administered at the cecum increases polyp detection: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2012;44:917–922. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1310009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tytgat GN. Hyoscine butylbromide: a review of its use in the treatment of abdominal cramping and pain. Drugs. 2007;67:1343–1357. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767090-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Behrens C, Stevenson G, Eddy R, Mathieson J. Effect of intravenous Buscopan on colonic distention during computed tomography colonography. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2008;59:183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Froehlich F. Colonoscopy: antispasmodics not only for premedication, but also during endoscope withdrawal? Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51:379. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(00)70065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Treweeke P, Barrett NK. Allergic reaction to Buscopan. Br J Radiol. 1987;60:417–418. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-60-712-417-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.de Brouwer EJ, Arbouw ME, van der Zwet WC, van Herwaarden MA, Ledeboer M, Jansman FG, ter Borg F. Hyoscine N-butylbromide does not improve polyp detection during colonoscopy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:835–840. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rondonotti E, Radaelli F, Paggi S, Amato A, Imperiali G, Terruzzi V, Mandelli G, Lenoci N, Terreni NL, Baccarin A, et al. Hyoscine N-butylbromide for adenoma detection during colonoscopy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45:663–668. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, Pham B, Klassen TP. Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses. Health Technol Assess. 1999;3:i–iv, 1-98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mui LM, Ng EK, Chan KC, Ng CS, Yeung AC, Chan SK, Wong SK, Chung SC. Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of intravenously administered hyoscine N-butyl bromide in patients undergoing colonoscopy with patient-controlled sedation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(03)02377-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Byun TJ, Han DS, Ahn SB, Cho HS, Kim TY, Eun CS, Jeon YC, Sohn JH. Role of Intravenous Hyoscine N-Butyl Bromide At the Time of Colonoscopic Withdrawal for Polyp Detection Rates: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:AB229. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee JM, Cheon JH, Park JJ, Moon CM, Kim ES, Kim TI, Kim WH. Effects of Hyosine N-butyl bromide on the detection of polyps during colonoscopy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:90–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Eide TJ. Risk of colorectal cancer in adenoma-bearing individuals within a defined population. Int J Cancer. 1986;38:173–176. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Winawer SJ. Colorectal cancer screening comes of age. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1416–1417. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305133281909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, O’Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, Waye JD, Schapiro M, Bond JH, Panish JF. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1977–1981. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Saunders BP, Williams CB. Premedication with intravenous antispasmodic speeds colonoscope insertion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;43:209–211. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Saunders BP, Elsby B, Boswell AM, Atkin W, Williams CB. Intravenous antispasmodic and patient-controlled analgesia are of benefit for screening flexible sigmoidoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;42:123–127. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:378–384. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Parra-Blanco A, Nicolas-Perez D, Gimeno-Garcia A, Grosso B, Jimenez A, Ortega J, Quintero E. The timing of bowel preparation before colonoscopy determines the quality of cleansing, and is a significant factor contributing to the detection of flat lesions: a randomized study. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:6161–6166. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rex DK. Colonoscopic withdrawal technique is associated with adenoma miss rates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51:33–36. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(00)70383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pickhardt PJ, Nugent PA, Mysliwiec PA, Choi JR, Schindler WR. Location of adenomas missed by optical colonoscopy. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:352–359. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-141-5-200409070-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rex DK, Bond JH, Winawer S, Levin TR, Burt RW, Johnson DA, Kirk LM, Litlin S, Lieberman DA, Waye JD, et al. Quality in the technical performance of colonoscopy and the continuous quality improvement process for colonoscopy: recommendations of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1296–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bond JH, Chally CH, Blackwood WD. A controlled trial of premedication with dicyclomine hydrochloride (Bentyl) in colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1974;21:61. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(74)73793-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Norfleet RG. Premedication for colonoscopy: randomized, double-blind study of glucagon versus placebo. Gastrointest Endosc. 1978;24:164–165. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(78)73496-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Waxman I, Mathews J, Gallagher J, Kidwell J, Collen MJ, Lewis JH, Cattau EL, al-Kawas FH, Fleischer DE, Benjamin SB. Limited benefit of atropine as premedication for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:329–331. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70725-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Munroe CA, Lee P, Copland A, Wu KK, Kaltenbach T, Soetikno RM, Friedland S. A tandem colonoscopy study of adenoma miss rates during endoscopic training: a venture into uncharted territory. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:561–567. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.11.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


