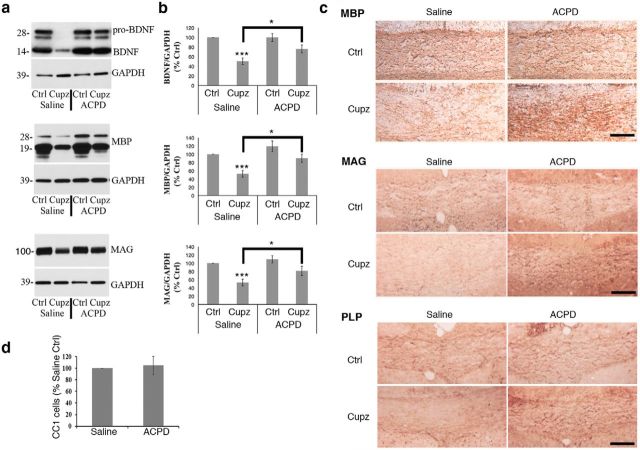
Figure 1.
Cuprizone-lesioned mice exhibit an increase in BDNF and myelin protein levels 6 h after a single stereotaxic injection of ACPD. a, Western blots demonstrate BDNF, MBP, and MAG protein levels in the corpus callosum of wild-type mice subjected to a 4 week cuprizone lesion and injected with ACPD or 0.9% saline vehicle. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. b, Graphs represent a densitometric analysis of Western blots normalized to GAPDH and are presented as percentage saline-injected control. Levels of mature BDNF are indicated in this analysis. c, Immunohistochemical analysis of MBP, MAG and PLP reactivity in the corpus callosum reveals strong staining intensity in the intact corpus callosum that is decreased following exposure to cuprizone. This MBP, MAG, and PLP deficit is reversed in cuprizone-lesioned animals 6 h after the administration of ACPD. Western blot data analyzed by ANOVA; ***significantly different from saline-injected control at p < 0.0005; *significantly different at p < 0.02. Each Western blot lane is from the corpus callosum of a single mouse within one experiment. Each experiment was repeated eight times. Scale bar, 100 μm. d, Quantification of CC1+ oligodendrocytes in the lesioned corpus callosum revealed that ACPD injection does not affect CC1+ cell numbers; N = 3.