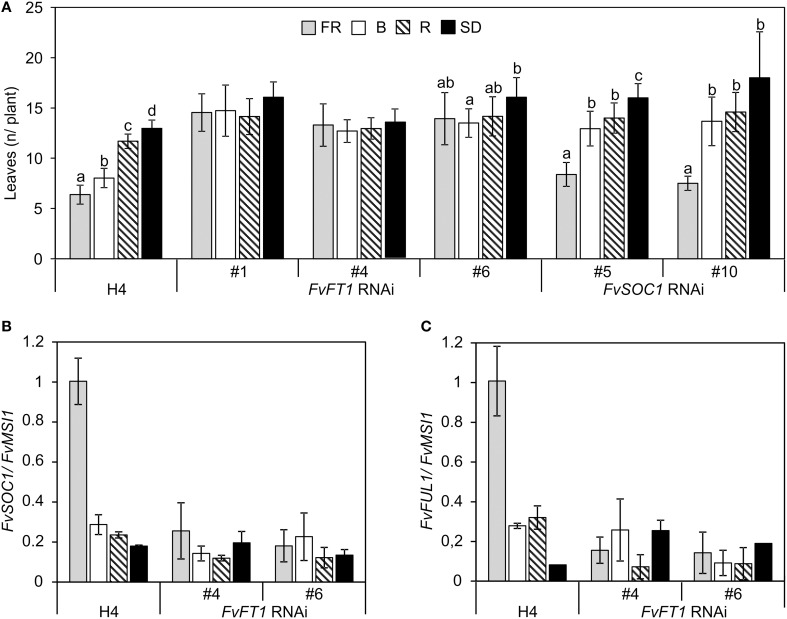
Figure 3.
RNAi silencing of FvFT1 and FvSOC1 affects the regulation of flowering by light quality in the perpetual flowering F. vesca accession Hawaii-4 (H4). (A) Flowering time of H4, and FvFT1 and FvSOC1 RNAi lines in different end-of-day light quality treatments indicated as the number of leaves in the primary leaf rosette before the terminal inflorescence (n = 11–23 for FvFT1 RNAi lines, n = 28–30 for H4, n = 13–18 for FvSOC1 RNAi-5, n = 5 for FvSOC1 RNAi-10). Flowering results were subjected to Two-Way ANOVA (p < 0.001 for each treatment, genotype, and treatment × genotype interaction). Pairwise comparisons were carried out for every genotype separately using Tukey's test, α = 0.01. Treatments with different letters indicate significant differences within the genotype. (B) Relative expression of FvSOC1 and (C) FvFUL1 in the shoot apex samples of Hawaii-4 and FvFT1 RNAi lines. T1 and H4 seedlings with 3–4 open leaves were subjected to 12-h short-day (SD) or 12-h SD plus 6-h low intensity (15 μmol m−2s−1) end-of-day treatment with far-red, red or blue light (FR, R, and B, respectively) at 22°C for 7 weeks. For gene expression data, three biological replicates were analyzed by real-time PCR. Shoot apex samples were collected 4 h after dawn. All results are mean ± SD