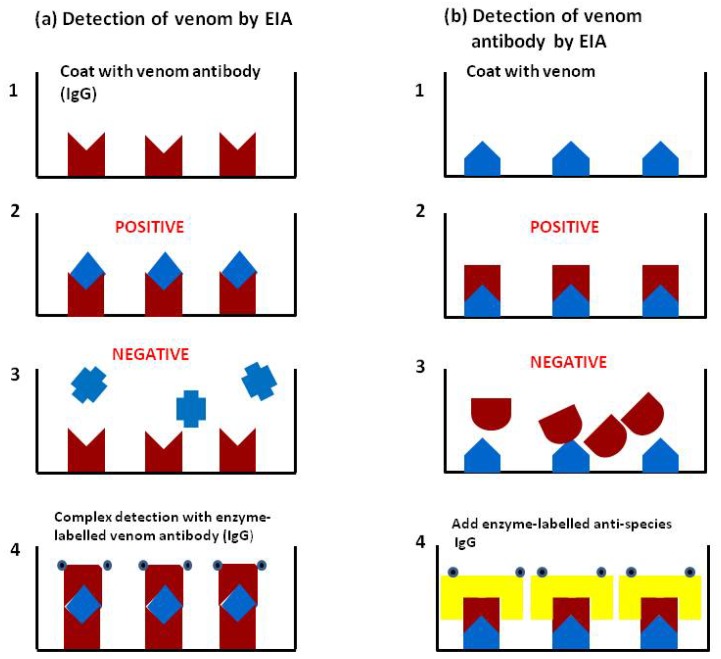
Figure 5.
(a) Detection of venom by EIA (ELISA): (1) Well of microtitre plate is coated with specific venom antibody IgG (or other immunoglobulin fragment such as Fab or F(ab/)2); (2) Patient’s sample containing specific venom is added to the well and binds to the antibody; (3) Patient’s sample containing a different venom is added and the venom is not recognised by the antibody and therefore does not bind; (4) In the positive sample the antigen/antibody complex is detected using enzyme-labelled antibody IgG; (b) Detection of venom antibody by EIA: (1) Plate is coated with venom; (2) Patient’s sample containing specific venom antibody added and binds to the venom; (3) In negative sample no binding occurs; (4) In the positive sample, venom/antibody complex is detected using enzyme-labelled anti-species IgG. It should be noted that there is a washing step between each stage of the assay to remove unbound components.