Figure 5.
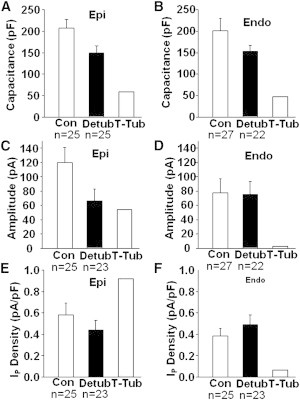
EPI and ENDO differences in T-system IP. (A) In detubulated cells (Detub), cell capacitance (Cm) declined 28% in EPI. T-system (T-Tub) membrane capacitance, and hence the membrane area, was calculated to be the difference between Con and Detub Cm. (B) Cm decreased by 23% in ENDO. T-Tub membrane capacitance was calculated as in panel A. (C) Detubulation caused a significant decrease in EPI IP amplitude. Taking the difference between Con and Detub IP amplitudes yielded T-Tub IP amplitude. (D) Detubulation minimally decreased ENDO IP amplitude. T-Tub IP was calculated as in panel C. (E and F) IP membrane density for total cell (Con), cell surface (Detub), and T-Tub were calculated by dividing the IP amplitude by the corresponding Cm. The density of IP in T-system membranes appears to be much higher than that in surface cell membrane, but in ENDO most of T-system IP is inhibited by endogenous A2.
