Figure 4.
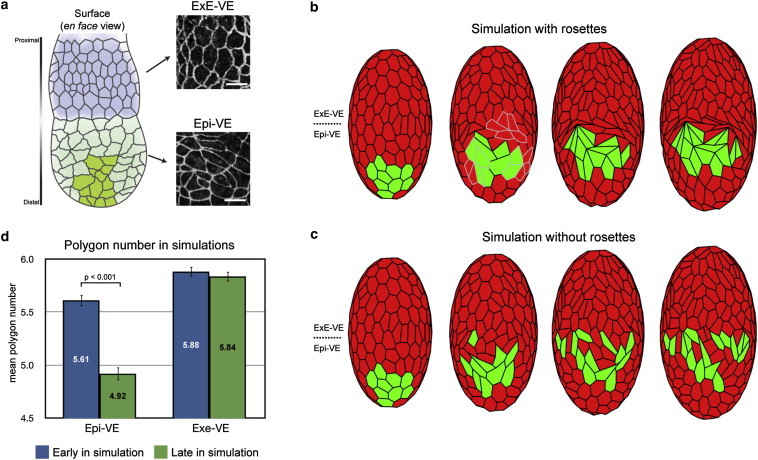
Simulation of AVE cell migration in the mouse VE with and without rosettes. (a) Schematic diagram of the visceral endoderm (VE) of a mouse egg-cylinder. The portions of the VE that cover the extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE-VE, blue) and that cover the epiblast (Epi-VE, green) as well as the proximally migrating AVE cells (dark green) are indicated. Differences in cell shapes are illustrated by high magnification views of the VE of an egg-cylinder stage mouse embryo stained with the tight junction marker ZO-1. (b) Snapshots of vertex model simulations of the mouse VE where rosettes are allowed to form (highlighted in gray), showing AVE cells (green) migrating in a single group. (c) As in panel b, but where rosettes are not allowed to form, showing AVE cells dispersing. (d) Comparison of mean polygon number in the ExE-VE and Epi-VE early and late in model simulations (corresponding to before and during AVE migration), recapitulating the experimentally observed reduction in mean polygon number in the Epi-VE. Images reproduced from Trichas et al. (23).
