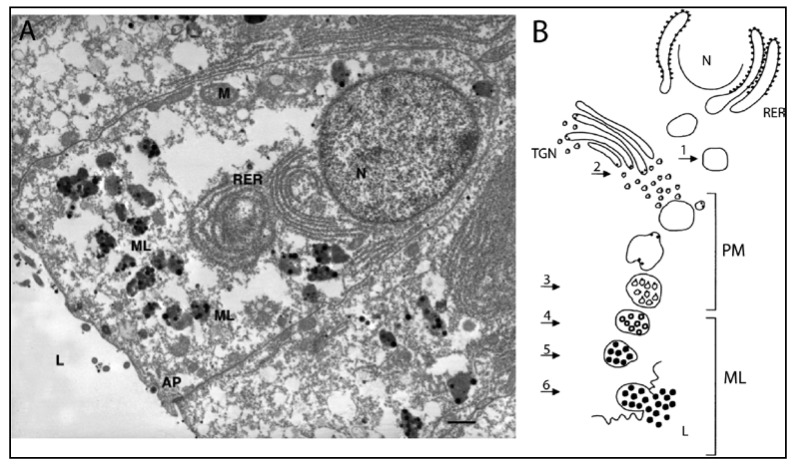
Figure 5.
Melanocytes and melanogenesis in the ink glad of Sepia. (A) Transmission electron micrograph of a melanin-producing cell in the epithelium of an ink gland. The cell’s apical pole (AP) faces the lumen of the ink gland (9 of Figure 4C), and the nucleus (N) is near the basal pole. Melanosomes (ML) containing melanin (black dots) are located between the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and the AP. Bar, 1 μM (From Palumbo [57], photo by A. Di Cosmo, used with permission); (B) Schematic diagram of melanin formation in a cell as in A. Steps 1–6 are described in the text. M, mitochondrion; PM, premelanosome; TGN, trans-Golgi network. Black dots in Steps 1 and 2 represent catalytic sites of melanogenic enzymes (Reproduced with permission from Palumbo [57], Copyright © 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.).