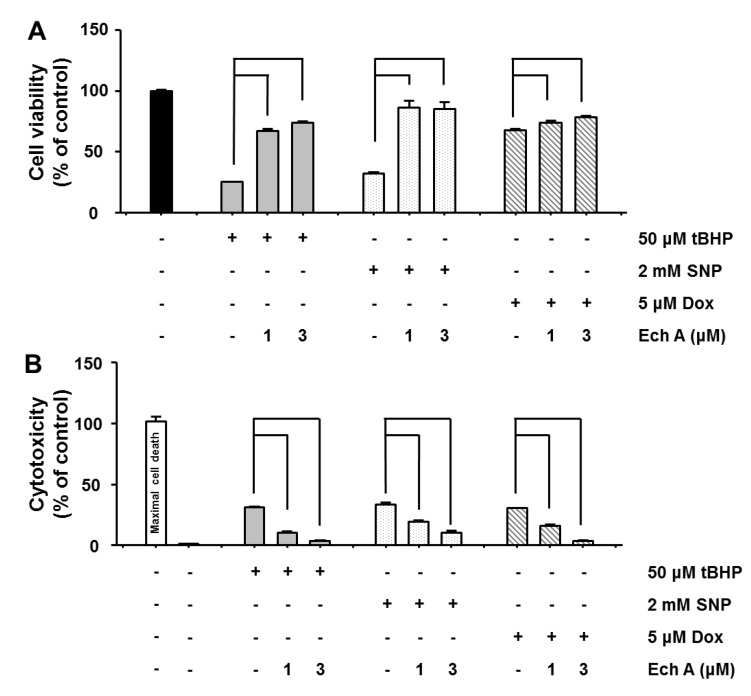
Figure 2.
Ech A inhibited cardiotoxic agent-induced cell death. (A) Rat cardiac myoblast H9c2 cells were treated with cardiotoxic agents (50 μM tBHP, 2mM SNP, or 50 μM tBHP) for 24 h, and cell survival rates were measured using an MTT assay. Cardiotoxic agents significantly reduced cell survival rate, but co-treatment with Ech A (1 or 3 μM) significantly prevented this drug-induced cell death. (B) In addition, cardiotoxic agents significantly induced cytotoxicity, but co-treatment with Ech A significantly prevented cardiotoxicity agent-induced cytotoxicity. Positive control was maximal cell death which was indicated by cells treated with cell lysis solution (digitonin solution). Negative control was untreated cells. Four independent in vitro experiments were performed. P < 0.05 vs. cardiotoxic agent single treatment group.