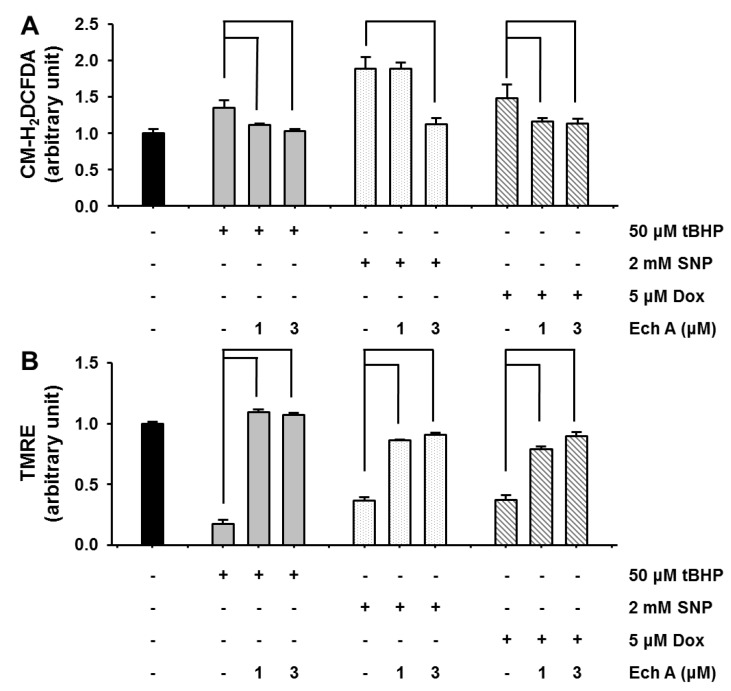
Figure 3.
Ech A attenuated cardiotoxic agent-induced mitochondrial damage in H9c2 cells. Cells were treated with cardiotoxic agents for 1 h, after which ROS level and mitochondrial membrane potential were measured using a microplate assay. (A) Cardiotoxic agents rapidly increased ROS (CM-H2DCFDA) level and (B) decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm, TMRE). Co-treatment with Ech A attenuated the increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) level and preserved mitochondrial membrane potential. Four independent in vitro experiments were performed. P < 0.05 vs. cardiotoxic agent single treatment group.