Fig 3. DNA damage signaling is attenuated in set2Δ.
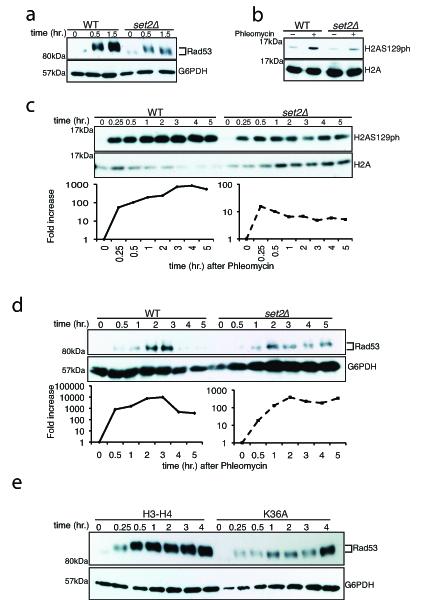
Log-phase cells were exposed to phleomycin for indicated times and whole cell extract was prepared (see Methods). (A) Diminution in Rad53 hyper-phosphorylation at indicated time-periods in a set2Δ after phleomycin treatment. The antibody to Rad53 is against the entire protein and G6PDH is used as a loading control. (B) Abrogated γ-H2A.X activation in set2Δ after phleomycin (50 μg/mL) treatment for two hours. (C) Time-course showing the activation of γ-H2A.X after phleomycin treatment. Quantification (H2AS129ph/H2A) of the Western blot is shown below. (D) Activation of Rad53 was monitored after phleomycin treatment in WT and set2Δ. Quantification (Rad53/G6PDH) of the Western blot is shown below, which reveals abrogated DNA damage checkpoint activation in set2Δ (plotted as a semi-log plot). (E) H3K36A mutant cells also show abrogated DNA damage checkpoint activation as monitored by Rad53 activation kinetics. Representative western blots, from at least 3 biological replicates), are presented.
