Fig 4. Temporal regulation of H3K36me3 and H3K36me2 correlates with proteasome-mediated degradation of Set2.
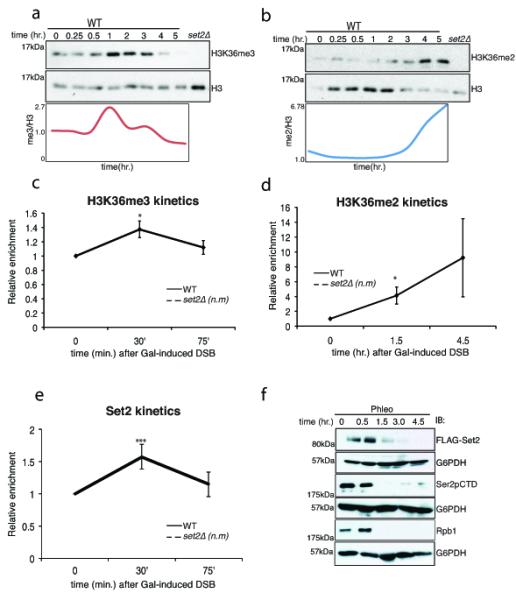
Immunoblots showing the levels of (A) H3K36me3 and (B) H3K36me2 after DSB induction by phleomycin. Exponentially growing yeast cells were exposed to phleomycin for indicated times and whole cell extract was prepared. (C) H3K36me3 is transiently induced near the site of DSB (assessed by ChIP at 0.2 kb), at early time-points. The error bars represent ± s.e.m from two different biological replicates. n.m. represents ‘not measurable’ (D) H3K36me2 is induced near the site of DSB (assessed by ChIP at 0.2 kb), at later time points. The error bars represent ± s.e.m from two different biological replicates. n.m. represents ‘not measurable’ (* represents p <0.05 for 4C and 4D). (E) Preferential enrichment of Set2 near DSB (assessed by ChIP at 0.2kb from DSB). n.m. represents not measurable (*** represents p<0.01). (F) Time course experiment after phleomycin treatment for Set2 (FLAG-Set2), Ser2pCTD (elongating RNA Polymerase II) and Rpb1 (largest subunit of RNAPII). G6PDH is used as loading control.
