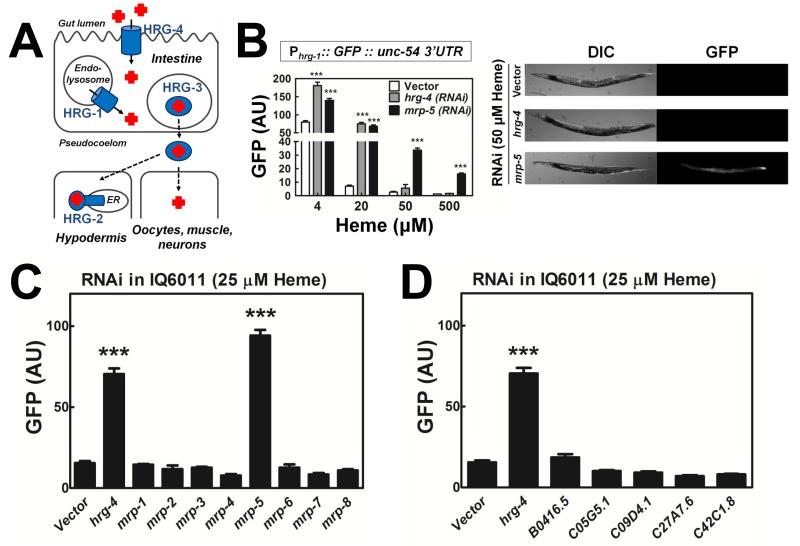
Figure 1. mrp-5 is an essential regulator of C. elegans heme homeostasis.
(A) Current model of heme homeostasis pathways in C. elegans. HRG-1/4 proteins import heme into the cytosol of intestinal cells, HRG-3 is secreted from the intestine for heme delivery to other tissues, and HRG-2 is a resident ER protein involved in heme utilization within the hypodermis. (B) Loss of mrp-5 results in a heme depletion signal that can be rescued by dietary heme. LEFT: GFP fluorescence (60-120 worms per treatment) quantified using COPAS BioSort in IQ6011 (Phrg-1::GFP::unc-54 3′ UTR; unc119(ed3); unc-119 rescue fragment) exposed to vector, hrg-4, or mrp-5 by feeding RNAi at varying heme concentrations. ***P<0.001 when compared to vector control under the same conditions (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-test). RIGHT: Images of IQ6011 RNAi worms supplemented with 50 μM heme. (C) Loss of mrp-5, and no other mrp, results in a heme depletion signal in the heme sensor strain, IQ6011. GFP fluorescence (60-120 worms per treatment) quantified from the hrg-1 transcriptional fusion line (IQ6011) exposed to vector, or RNAi against an mrp gene at 25 μM heme. GFP was quantified using COPAS BioSort. ***P<0.001 when compared to vector control under the same conditions (one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-test). (D) RNAi of FLVCR1 homologs in C. elegans does not activate a heme depletion signal in IQ6011. GFP fluorescence in IQ6011 was measured as in Figures 1B and 1C. ***P<0.001 when compared to vector control under the same conditions (one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-test). See also Figure S1.