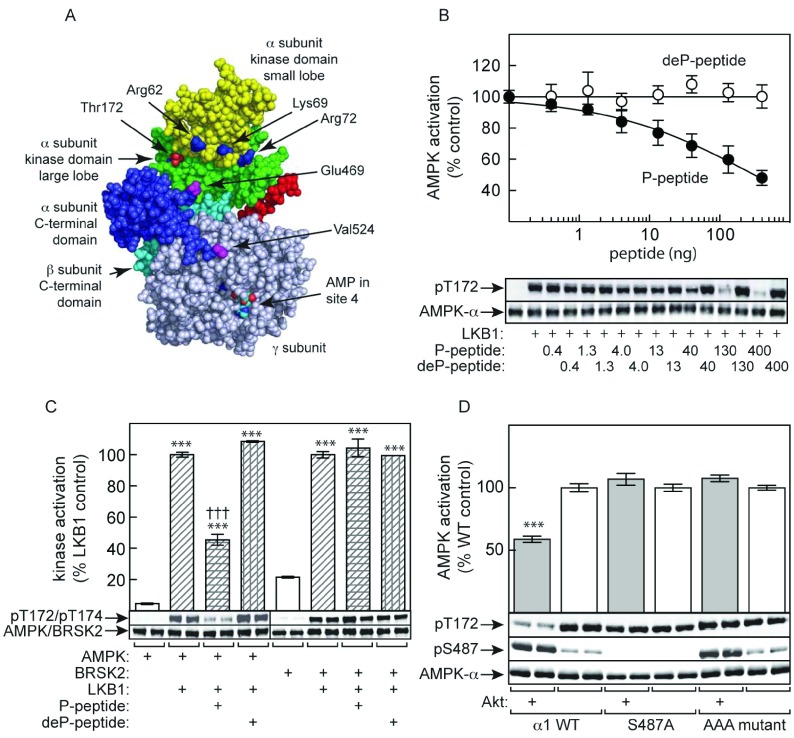
Figure 7. Evidence that the phosphorylated ST loop inhibits LKB1 phosphorylation by direct interaction with the kinase domain.
(A) Model for the structure of an AMPK heterotrimer (PDB code 2Y8L, space-filling model made using PyMOL; http:://pymol.org) showing the location of the ends of the ST loop (Glu469 and Val524), with Glu469 particularly close to Thr172; the intervening residues of the ST loop were deleted from the construct used to produce this structure. (B) Inhibition of activation of the human α1β2γ1 complex by LKB1 by peptide corresponding to the sequence from Arg466 to Asp525, either with (P-peptide) or without (deP-peptide) prior phosphorylation by Akt. Results are means±S.E.M. (n=4). (C) Inhibition of activation and phosphorylation by LKB1 of α1β2γ1 complex (left-hand side) and BRSK2 (right-hand side) by P-peptide and deP-peptide as in (B). Results for kinase activity are expressed as a percentage of activities obtained without either peptide, and are means±S.E.M. (n=2); ***P<0.001 relative to controls without LKB1; †††P<0.001 relative to control without P-peptide. Results of Western blots are from duplicate incubations. (D) Human AMPK (α1β2γ1 complex, either WT, S487A or AAA mutant) was incubated with LKB1 following prior incubation with ATP with or without Akt. AMPK activation (top panel) and phosphorylation of Thr172 and Ser487 (bottom panel) was monitored.