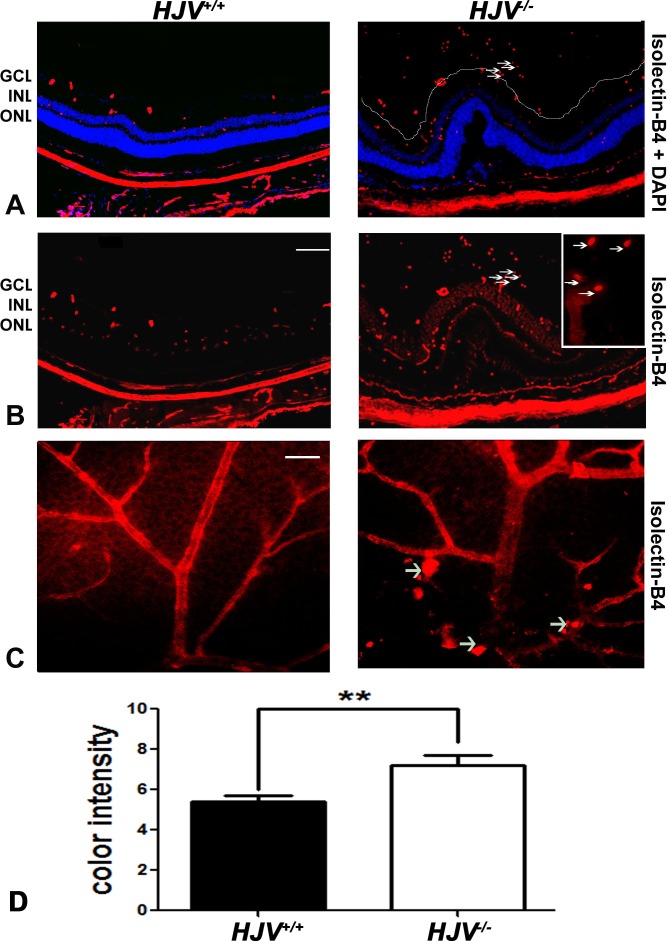
Figure 1.
Evidence of neovascularization in Hjv−/− mouse retinas as detected by isolectin-B4 staining. (A, B) Retinal cryosections from Hjv+/+ and Hjv−/− mice were incubated with biotinylated isolectin-B4, a specific endothelial cell marker, to label blood vessels. Blood vessels growing into the vitreous were detected in Hjv−/− mouse retina; arrows point to the same blood vessels observed in the vitreous of these mutant mice at low and high magnification. Calibration bar: 50 μm. (C) Retinal flat-mounts were stained with biotinylated isolectin-B4 to label retinal vasculature. Neovascular tufts and vascular masses (arrows) were observed in retinas of Hjv−/− mice compared with normal vasculature in retinas of wild-type mice. Calibration bar: 50 μm. (D) Quantification of the data obtained from metamorphic analysis of the color intensity of the retinas stained with isolectin-B4 (**P < 0.01, n = 3 mice for each genotype). ONL, outer nuclear layer.