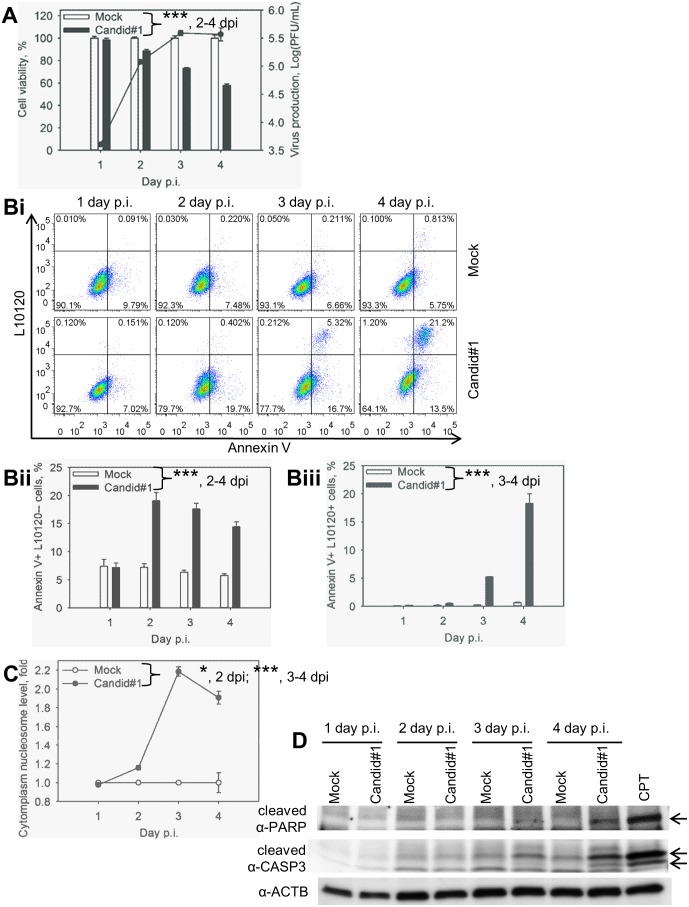
Figure 1. Candid#1 JUNV infection induces apoptosis in A549 cells.
Cells were mock-infected (Mock) or infected (MOI = 1.75 PFU/cell) with Candid#1. A. Reduction of cell viability in infected cells correlated with virus production. Production of infectious progeny and cell viability determined using plaque assay and MTT-based assay, respectively. Cell viability of mock-infected samples was assigned as 100%. B. Quantification of PS flipping. Cells were stained with FITC-Annexin V (Annexin V) and the viability dye L10120 and analyzed by FACS. Bi. Representative dot-plots. Annexin+L10120−cells (low right quadrant) represent the population of cells at early apoptotic stage. Annexin+L10120+cells (top right quadrant) represent apoptotic and dead cells. Bii. Percentage of cells at early stage of apoptosis. Biii. Percentage of apoptotic and dead cells. C. Accumulation of mono- and oligonucleosomes in the cytoplasm was determined by ELISA. For A, Bii, Biii and C, data represent the average of three replicates ±SEM. *** and * - P. value<0.001 or <0.05, respectively. D. Activation of CASP3 and PARP cleavage in infected cells. Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting for β-actin- (α-ACTB), CASP3 (α-cleaved CASP3) and PARP (α-cleaved PARP) cleavage. Arrows point to the cleaved form of PARP and CASP3. Camptothecin (CPT) was used as a positive control for apoptosis induction.