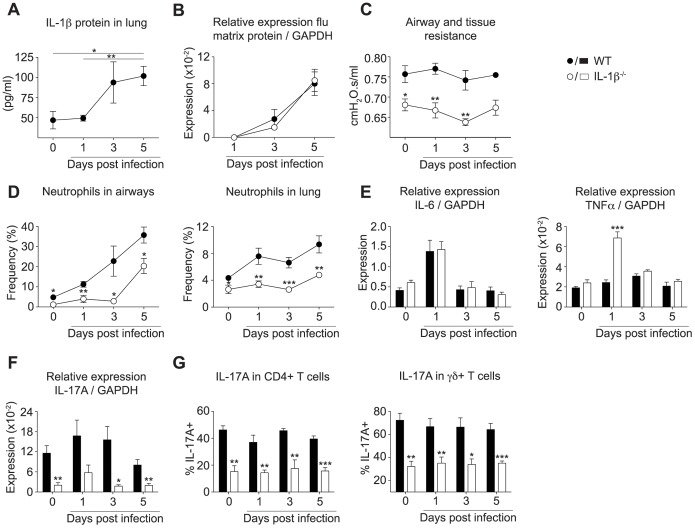
Figure 3. IL-1β mediated airway resistance, neutrophilic inflammation and IL-17A expression during influenza-induced exacerbations of COPD.
Exacerbation of COPD in C57BL/6 mice was induced as depicted in Figure 2A. (A) IL-1β protein in whole lung including airways and trachea following influenza infection (day 1–5) or PBS challenge (day 0) was assessed by ELISA. (B) Viral load in whole lung and trachea of wild type or IL-1β deficient animals was determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. (C) Airway and tissue resistance was measured by invasive plethysmography at indicated time points after infection. (D) The proportion of neutrophils in the airways and lung was determined by flow cytometry. Data are pooled from two independent experiments (n = 4–5). (E) Expression of IL-6, TNFα, and (F) IL-17A was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. (G) Proportion of IL-17A positive CD4+ T cells or γδ T cells was determined by flow cytometry after restimulation in vitro. All data are representative of at least two independent experiments (n = 4–5) and mean ± s.e.m. is shown.