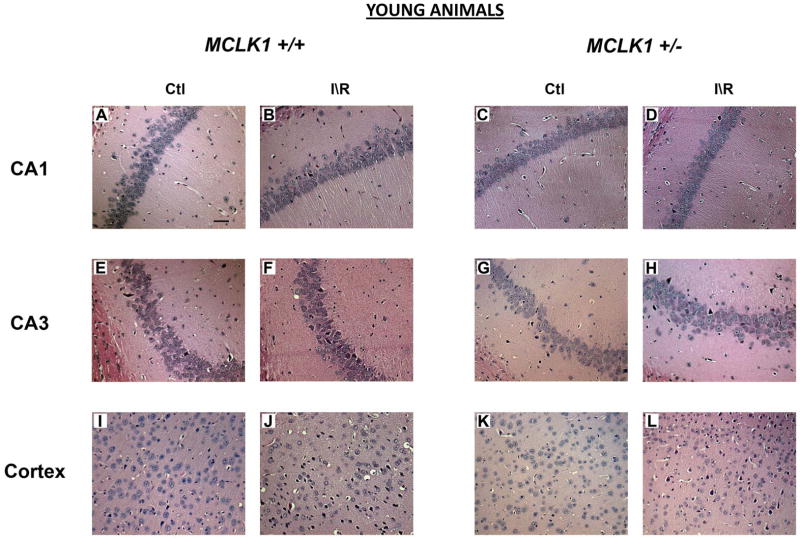
Figure 1.
Comparison of BCCAO-induced neuronal damage in hippocampus and cerebral cortex of young Mclk1+/+ and Mclk1+/− mice. The panels shown for both groups are representative hematoxylin/eosin-stained slides of the CA1 (A–D) and the CA3 (E–H) regions of the hippocampus and of a portion of the cerebral cortex (I–L). Sections of control (sham operated) and ischemia-reperfused animals were presented for each analyzed region (scale bar, 50 μm).