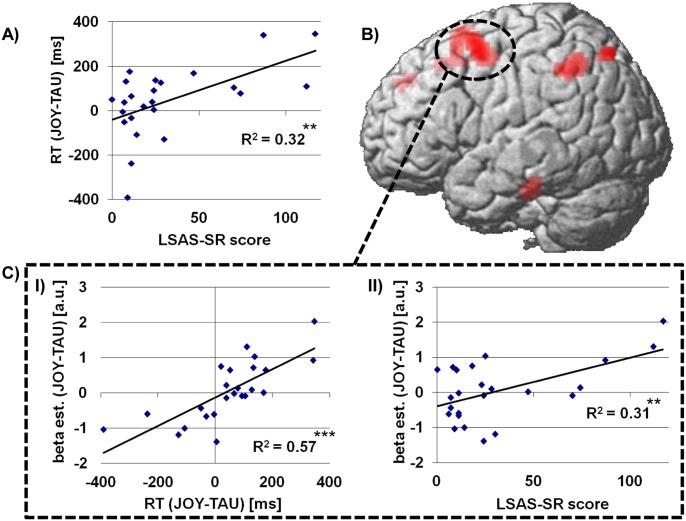
Figure 2. Behavioral and cerebral correlates of the negative attention bias during laughter perception in individuals with varying severity of social anxiety.
a) Linear relationship between LSAS-SR scores and faster response times to taunting (TAU) than to joyful (JOY) laughter, i.e. negative attention bias. b) Cerebral correlates of the negative attention bias in the left DLPFC (circled). Results are shown at a threshold of p<0.001, uncorrected at voxel-level, and a cluster extent of k>10 voxels; results in the DLPFC are significant with p<0.05, FWE-corrected for multiple comparisons across the whole brain at cluster level. c) ROI analysis of extracted mean parameter estimates in the left DLPFC (I) illustrates the linear association of the negative attention bias and cerebral activation during laughter perception and (II) demonstrates an additional positive linear association of differential responses to TAU and JOY in this region and LSAS-SR scores. Asterisks mark levels of significance: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.