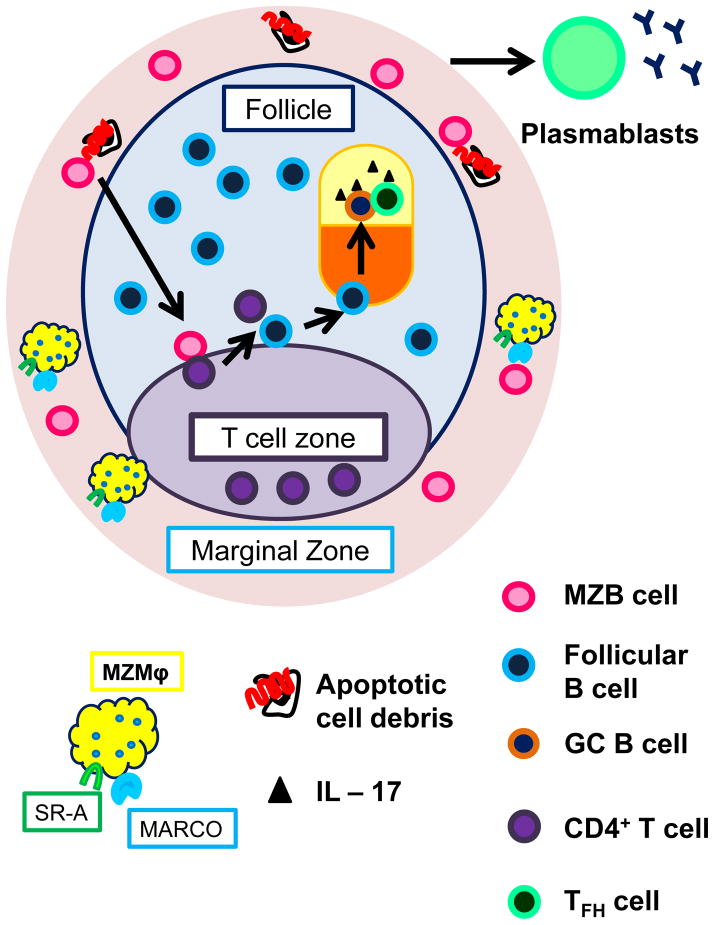
Figure 2.
Marginal zone macrophages (MZMϕ) retain MZB cells in the marginal zone and clear apoptotic cell debris. In their absence, such as in the BXD2 mouse, exposes autoreactive MZB cells to autoantigens from apoptotic cells. Such antigen-activated autoreactive MZB cells can either migrate to the red pulp and become short-lived plasmablasts or migrate into the follicle where they engage cognate CD4+ T cells from the T cell zone. Those activated CD4+ T cells can activate cognate follicular B cell, which proliferate in the follicle to form a germinal center (GC). Proliferating GC B cells undergo affinity maturation in the dark zone, then enter the light zone where it encounters follicular helper T (TFH) cells. TFH help induce the engaged B cell to undergo class switch and become either long lived antibody secreting plasma cells or memory B cells. Mountz’s group have shown in the BXD2 model that IL – 17 signaling arrests both TFH cells and GC B cells in the GC, and thereby prolongs GC reaction and promote antibody production.