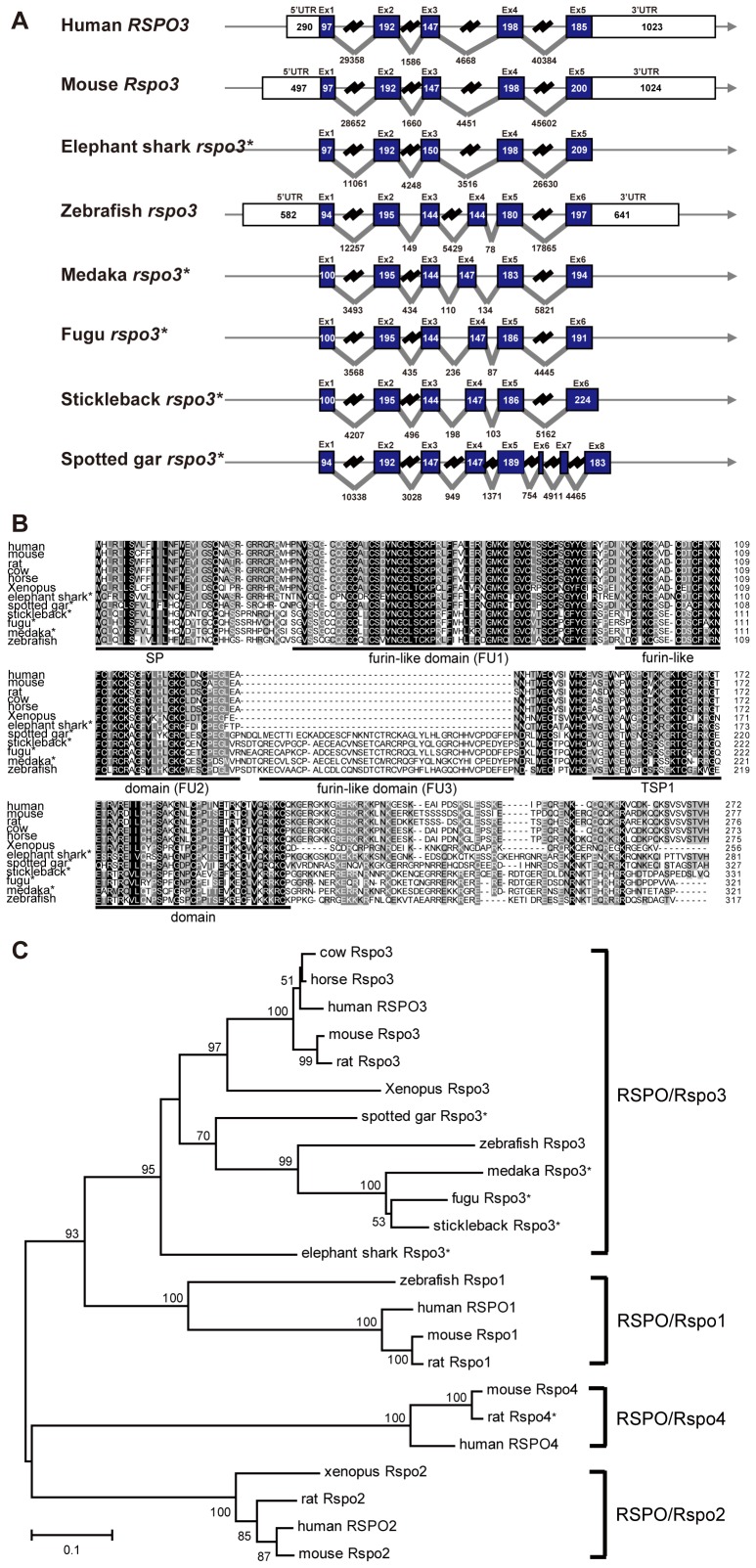
Figure 1. Gene structure, amino acid sequence, and phylogenetic analysis of zebrafish and other vertebrate Rspo3 orthologs.
(A) Comparison of human, mouse, elephant shark, zebrafish, medaka, fugu, stickleback, and spotted gar RSPO3/rspo3 gene structure. Exons are shown as boxes (filled box, protein coding region; open box, UTR). Introns are shown as lines. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of human, mouse, rat, cow, horse, Xenopus, elephant shark, spotted gar, stickleback, fugu, medaka, and zebrafish RSPO/Rspo3. The identical amino acids are in black and similar amino acids are in grey. Protein domains of zebrafish Rspo3 are shown using black lines, and the domain names are given. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of the RSPO/Rspo family using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method. The length of branches represents the genetic distances, and numbers on nodes are bootstrap percentages to indicate the two clades as sisters. The accession numbers are as follows: human RSPO1 NP_001033722.1, mouse Rspo1 NP_619624.2, rat Rspo1 NP_001101450.1, zebrafish Rspo1 NP_001002352.1, human RSPO2 NP_848660.3, mouse Rspo2 NP_766403.1, rat Rspo2 NP_001124047.1, Xenopus Rspo2 NP_001088999.1, human RSPO3 NP_116173.2, mouse Rspo3 NP_082627.3, rat Rspo3 NP_001094460.1, cow Rspo3 NP_001069502.1, horse Rspo3 NP_001103152.1, Xenopus Rspo3 NP_001123245.1, medaka Rspo3 ENSORLP00000007233, fugu Rspo3 ENSTRUP00000009202, stickleback rspo3 ENSGACG00000006080, elephant shark Rspo3 SINCAMP00000010032, spotted gar Rspo3 ENSLOCP00000020398, human RSPO4 NP_001025042.2, mouse Rspo4 NP_001035779.1, rat Rspo4 XP_006235323.1. *,Ensembl or GenBank predicted sequence.