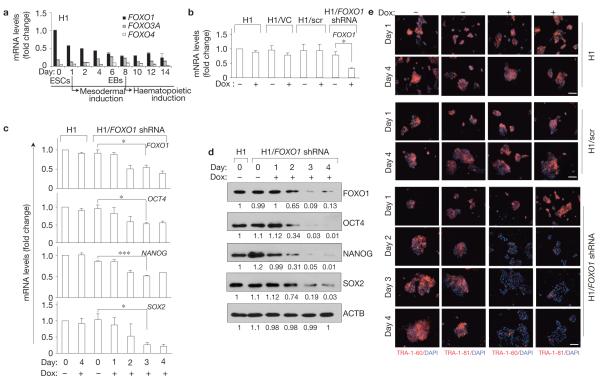
Figure 1.
FOXO1 is essential for the expression of hESC pluripotency markers. (a) qRT-PCR analysis of expression of FOXO genes in pluripotent undifferentiated hESCs and during mesodermal induction. The expression levels of FOXO3A and FOXO4 are relative to that of FOXO1 in undifferentiated H1 cells under self-renewal conditions. Note, downregulation of FOXO1 and upregulation of FOXO3A during differentiation of hESCs. FOXO6 expression was not detectable in hESCs. EBs, embryoid bodies. (b) FOXO1 expression was analysed by qRT-PCR in parental H1 hESCs and in H1 cells expressing shRNA targeting FOXO1 (H1/FOXO1 shRNA) cultured in the absence or presence of doxycycline (Dox) for 4 days under undifferentiated self-renewal conditions. H1 cells expressing vector control (H1/VC) or scrambled FOXO1 shRNA (H1/scr) were used as controls. (c) qRT-PCR analysis carried out as in b at the indicated times in cells treated with or without doxycycline. Quantification of the target genes was relative to the endogenous ACTB (-actin) transcript levels. Results are mean s.e.m. of three independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate (a-c); *P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, P < 0.001 (b,c). (d) An aliquot of cells from c was subjected to western blot analysis of the indicated proteins; relative intensities of bands are shown below each panel relative to that measured at time 0 in H1 cells (uncropped scanned gels are shown in Supplementary Fig. S12). (e) hESCs were cultured with or without doxycycline for the indicated times and immunostained for surface markers of pluripotency, TRA-1-60 and TRA-1-81, and counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars, 100 μm.