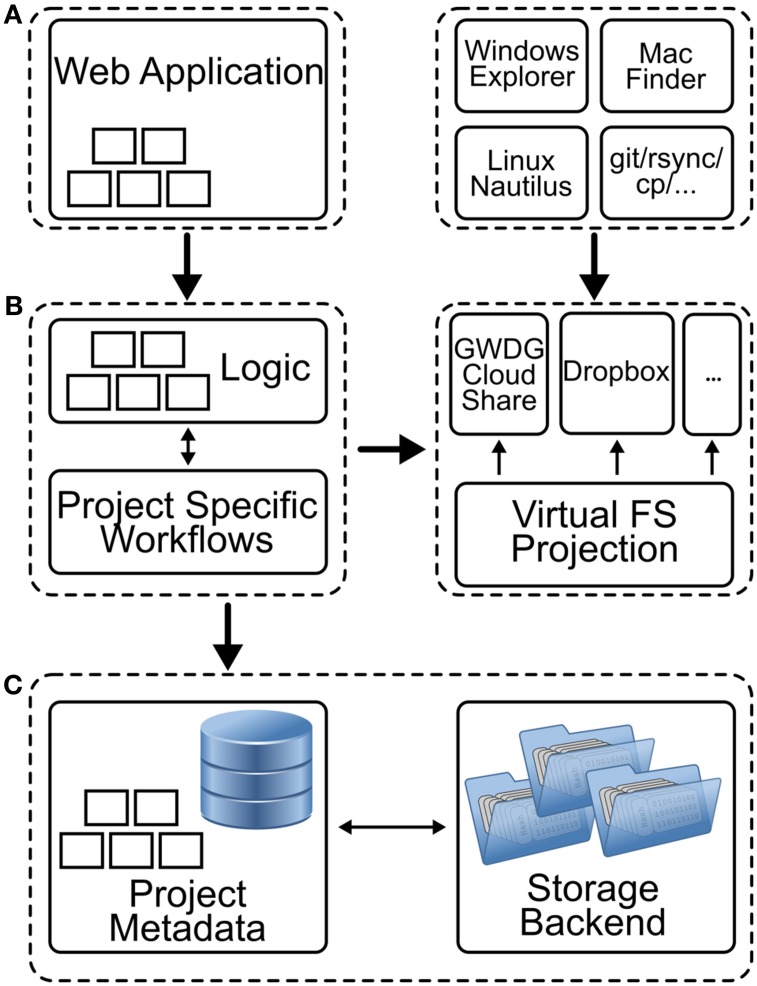
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the different components of NeuronDepot. (A) The graphical user interface consists of two parts: a web application and local applications. The web application (left) provides forms for assigning data, enter metadata, and annotating data with metadata. The upload and download processes are handled by GWDG Cloud Share incorporated by the filesystem projection layer (see below). Here, scientists can use established tools like Windows Explorer, Mac Finder, Linux Nautilus, or other file managers to copy files for upload in dedicated folders (right) which are connected to the cloud services. (B) The business logic (left) encodes the NeuronDepot logic rules that determine how data can be created, red, updated, and deleted. Moreover, when new data items are added, deleted, or modified, project-specific workflows can be triggered for each processing stage (illustrated by five small rectangles). A Virtual Filesystem Projection layer (right) maps data items and directories to GWDG Cloud Share synchronization clients based on project-specific metadata and provides a consistent view of the file system structure. (C) Within a project database additional metadata are stored. This can be metadata which was extracted by a computational workflow or manually entered data. The responsibility of the storage backend is to consistently store data items and provide abstractions for the file system projection layer.