Figure 1.
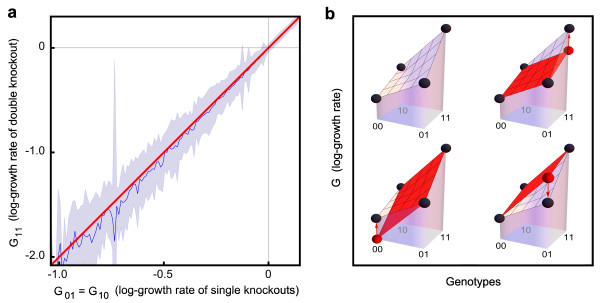
The log growth rates of two mutations combine additively. (a) The average effect of a double knockout (G11) as a function of the effects of the single knockouts (G01 and G10) is G11 = G01 + G10. Experimental mean +/- standard deviation (blue line and blue shaded area) and prediction of the additive null model (red line). (b) Given two mutations, there are four possible mutants with their corresponding log growth rates (black dots). If three of the four log growth rates are known, the fourth one can be predicted by a linear extrapolation (red plane), and epistasis can be defined as the linear deviation from such prediction (red arrow). The magnitude of the deviation is the same regardless of which three of four mutants are chosen.
