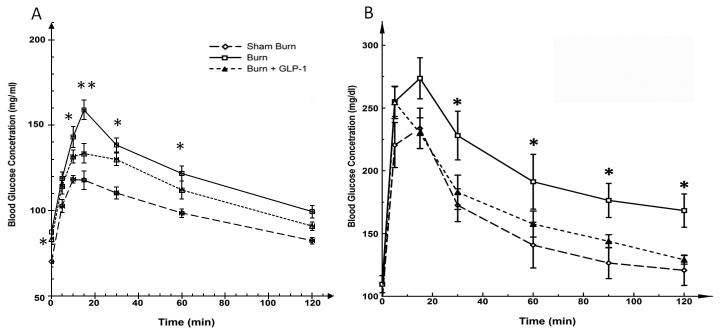
Figure 1.
A; Blood Glucose Levels during IGGTT. Fasting glucose levels were significantly different among the groups. B showed the highest level and it was reduced in B+GLP-1 animals. At time points 10, 15, 30, 60 min, plasma glucose levels were significantly higher in the B group, as compared with the SB and B+GLP-1 groups. 1B: Blood Glucose Levels with IPGTT. The blood glucose curves in Figures 1A and 1B showed a similar pattern, confirming the efficiency of GLP-1 in reducing burn injury induced hyperglycemia. The IGGTT study demonstrated a significantly lower level of maximal blood glucose compared with the IPGTT study in all groups of animals, demonstrating the difference of blood glucose responses to different routes of glucose administration.