FIG 2.
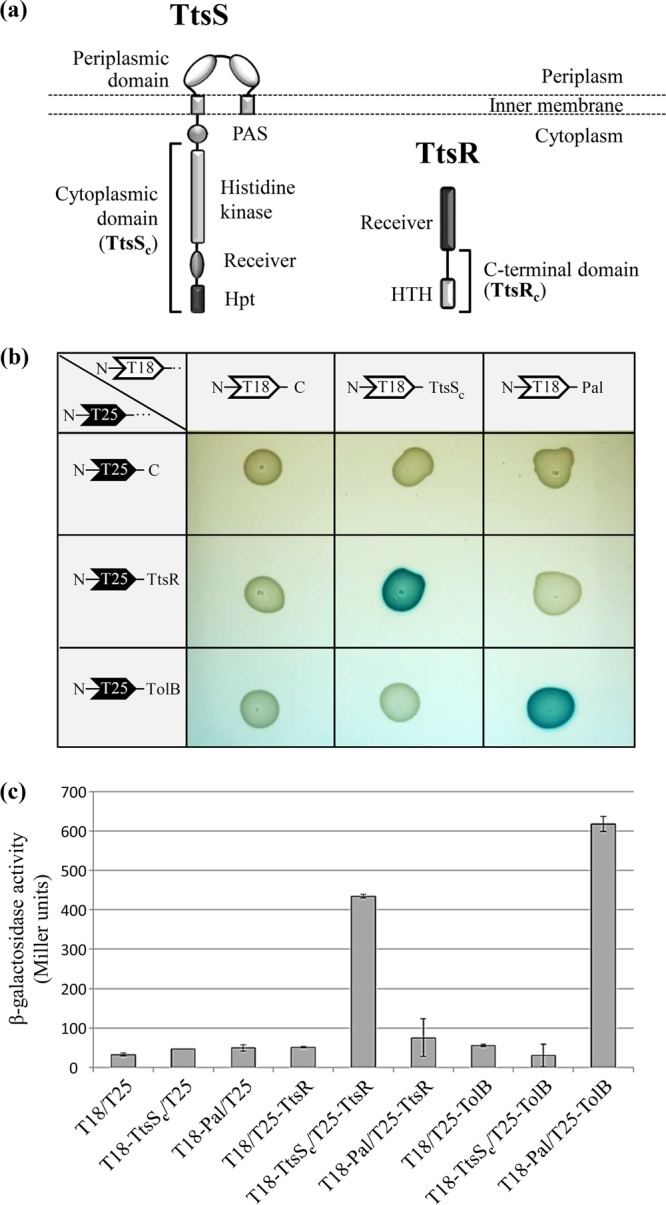
TtsS and TtsR interact together to form a two-component system. (a) Modular structures of the unorthodox sensor TtsS and the response regulator TtsR. The cytoplasmic domain of TtsS (TtsSc) and the C-terminal domain of TtsR (TtsRc) used for transcriptional and secretion experiments are indicated by brackets. All the other characteristic domains of the unorthodox sensor and NarL-type response regulator are indicated (Hpt for histidine phosphotransferase and HTH for helix-turn-helix). (b) Binary interactions between TtsSc and full-length TtsR determined by using the BACTH assay. TtsSc and TtsR were fused to the C termini of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase fragments T18 and T25, leading to plasmids pT18-TtsSc and pT25-TtsR. Various T18 and T25 plasmid combinations were cotransformed into E. coli cya strain BTH101 and plated onto LB agar–IPTG–X-gal medium. Functional complementation between the T18 and T25 fragments, which occurs only upon interactions of the hybrid proteins, triggers the expression of the cya gene and yields blue colonies. The E. coli TolB and Pal interacting proteins were used as a positive control. (c) Interactions were quantified by β-galactosidase assays in biological triplicates for all tested interactions.
