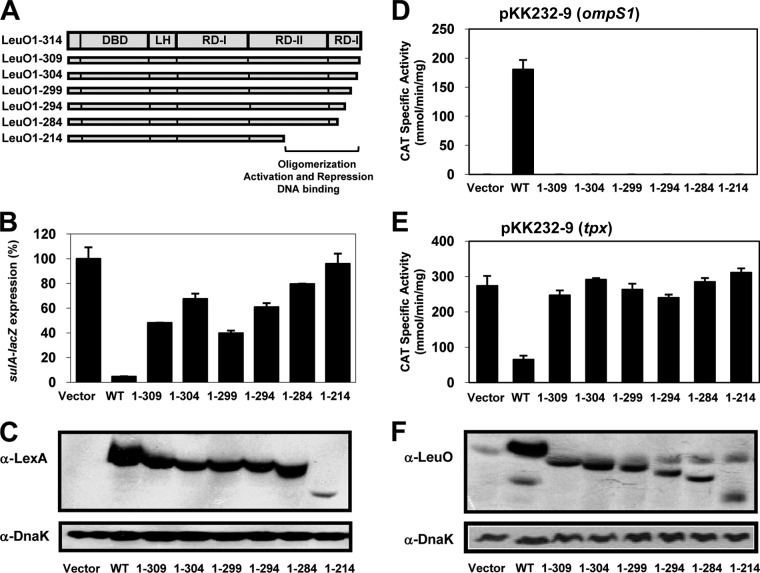
FIG 6.
Analysis of dimerization and regulatory functions of LeuO wt and C-terminal deletion mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the domains of the LysR family: DBD, LH, and the C-terminal regulatory domain with two subdomains, RD-I (central, C terminal) and RD-II. The localization of the deletions in the C-terminal domain is also shown. (B) Dimerization analysis. sulA::lacZ expression in strain SU101 carrying pSR658-A (vector), the expression of which was set equal to 100%, or carrying pLexA-LeuO (wt), pLexA-LeuO1-309, pLexA-LeuO1-304, pLexA-LeuO1-299, pLexA-LeuO1-294, pLexA-LeuO-1-284, or pLexA-LeuO1-214 is shown. (C) Expression of the LeuO wt and deletion mutants fused to LexA was evaluated by Western blotting using an anti-LexA polyclonal antibody and an anti-DnaK monoclonal antibody as a control after SDS-PAGE. The cultures were grown in LB medium to an OD600 of 1.0, and LexA-fused protein expression was induced with IPTG (1.0 mM). (D and E) Transcriptional profiles of fusions to the cat reporter gene for the ompS1 and tpx genes in S. Typhi in the presence of either the LeuO wt or mutants with different deletions in the C terminus: LeuO1-309, LeuO1-304, LeuO1-299, LeuO1-294, LeuO1-284, and LeuO1-214. (F) Expression of the LeuO wt and the deletion mutants was evaluated by Western blotting using an anti-LeuO polyclonal antibody and an anti-DnaK monoclonal antibody as a control. The cultures were grown in MA medium to an OD595 of 1.0, and expression of the proteins was induced with IPTG (100 μM).