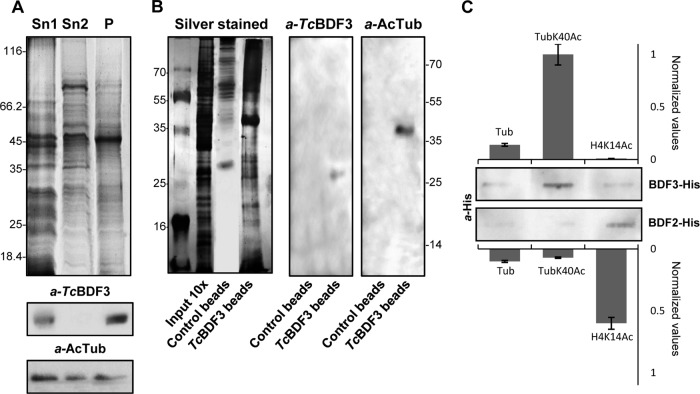
FIG 6.
TcBDF3 interacts with acetylated α-tubulin. (A) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE and Western blot analyses of epimastigote protein extracts enriched in cytoskeletal and flagellar proteins. Sn1, soluble protein extracts; Sn2, soluble cytoskeletal and flagellar protein extracts; P, insoluble cytoskeletal and flagellar protein extracts (50 μg per well). Rabbit anti-TcBDF3 antibodies (α-TcBDF3) and mouse anti-acetylated α-tubulin antibodies (α-AcTub) were used. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation assay using purified anti-TcBDF3 antibodies covalently coupled to magnetic beads (TcBDF3 beads). Magnetic beads coupled to IgGs (purified from antisera of nonimmunized rabbits) were used as a negative control (Control beads). On the left is a silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel of total cytoskeletal extracts and the elutions obtained after the immunoprecipitation experiment. On the right is a Western blot analysis of the eluted proteins after coimmunoprecipitation using purified rabbit anti-TcBDF3 antibodies (α-TcBDF3) and mouse monoclonal anti-acetylated α-tubulin antibodies (α-AcTub). (C) Slot far-Western blot assay. Acetylated tubulin (TubK40Ac), nonacetylated tubulin (Tub), and acetylated histone H4 (H4K14Ac) peptides were blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and incubated with His-tagged recombinant TcBDF3 (BDF3-His) or TcBDF2 (BDF2-His). Bound recombinant proteins were detected with anti-histidine antibodies (α-His). Signals were quantified by densitometry and normalized using the interaction with acetylated α-tubulin peptide as a reference (assigned the arbitrary value of 1). The bars and error bars indicate means ± standard deviations (SD) from the results of three independent experiments.