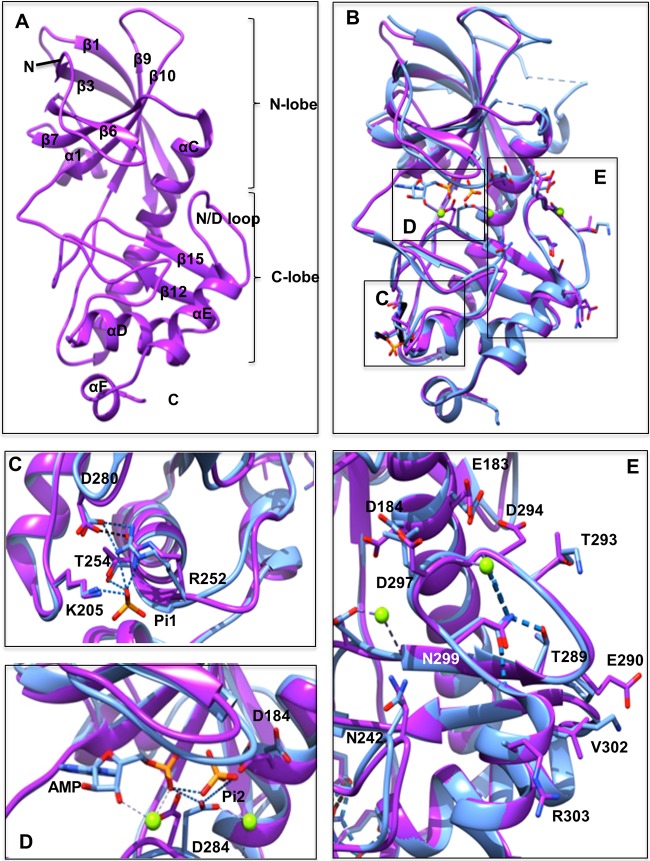
FIG 1.
Comparison of the eEF2K homology model and the MHCK A structure. (A) Front view of the homology model for eEF2K (purple) with the β-strands and α-helices numbered according to the sequence alignment with TRPM7-CAT. The kinase domain consists of small and large lobes, named the N and C lobes. N and C termini are indicated. (B) Front view of the superimposed homology model of eEF2K (purple) and the structure of MHCK A (blue) (PDB code 3lkm). Amino acid residues, AMP, and two phosphate (Pi) molecules (Pi1 and Pi2) are shown as sticks, and Mg2+ ions are shown as green spheres. The location of the Pi pocket, active site, and N/D loop in the context of the entire structure of MHCK A and the eEF2K homology model are highlighted by boxes labeled C to E, which are shown in greater detail in panels C to E. (C) A detailed view of the Pi pocket. The phosphate molecule (Pi1) interacts with the side chains of Arg252 (Arg734 in MHCK A), Thr254 (Thr736), and Lys205 (Lys684). This is indicated by the blue dashed lines. The salt bridge between Arg252 (Arg734) and Asp280 (Asp762) is shown as a black dotted line. (D) Detailed view of the active site. The residue Asp284 in the active site of eEF2K is located in a position similar to that of Asp766 in MHCK A. This residue in MHCK A forms hydrogen bonds with the phosphate molecule (Pi2), the α-phosphate of AMP, and Mg2+ in the active site pocket. These hydrogen bonds are shown as blue dashed lines. (E) Detail of the N/D loop. The position of Asn299 in eEF2K is essentially identical to that of Asn781 in MHCK A. Hydrogen bonds between Asn781 (Asn299) and Thr771 (Thr289), Gly776 (Asp294), Gly783 (Gly301), and Mg2+ are shown as blue dashed lines.