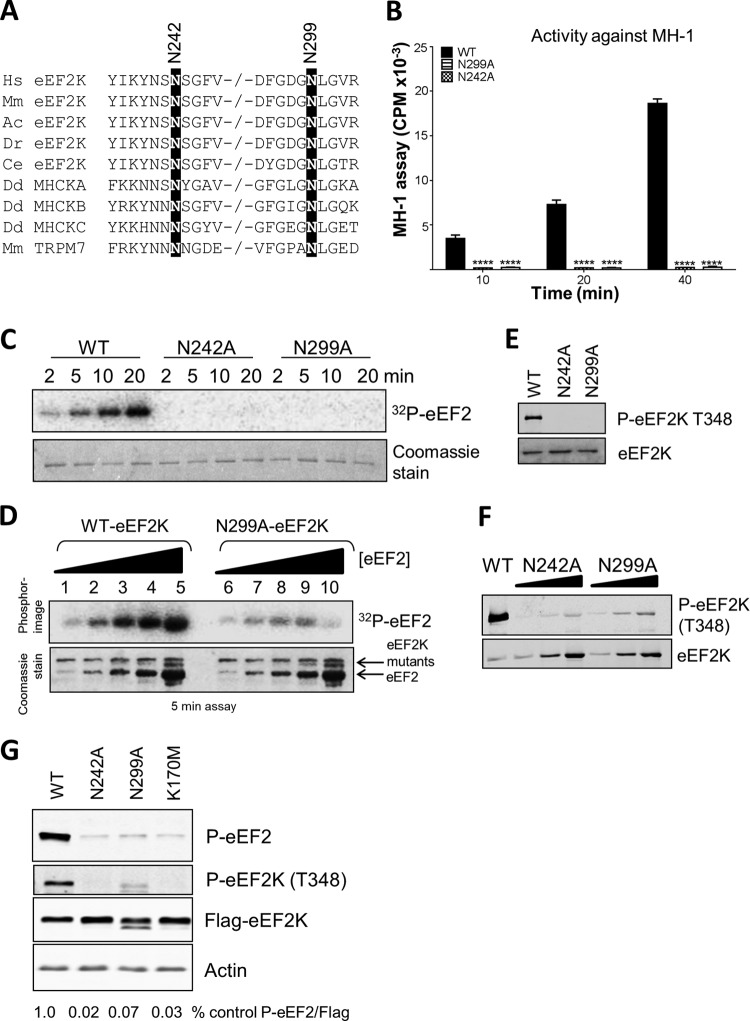
FIG 5.
Mutations at asparagine residues in the N/D loop of eEF2K. (A) Alignment of relevant regions of selected eEF2K sequences and certain other α-kinases, with conserved residues of interest indicated by black boxes. −/− indicates a gap in the sequence. Abbreviations for species are given in the legend to Fig. 2. (B) Activities of selected point mutants against MH-1. All assays were performed within the linear range of the assay. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3). ****, P < 0.0001. (C) Activities of selected point mutants against eEF2. (D) The activities of WT and N299A against increasing concentrations of eEF2. (E and F) Level of autophosphorylation determined by SDS-PAGE and Western blot using the phospho-Thr348 antibody. (F) HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding FLAG-tagged wild-type eEF2K or the N242A, N299A, or K170M mutants. Twenty-four hours later, cells were lysed, and equal amounts of protein were analyzed for p-eEF2, phospho-Thr348, FLAG (for eEF2K expression), or actin (loading control). The figures below each lane indicate the level of eEF2 phosphorylation, normalized to the signal for FLAG, as a ratio.