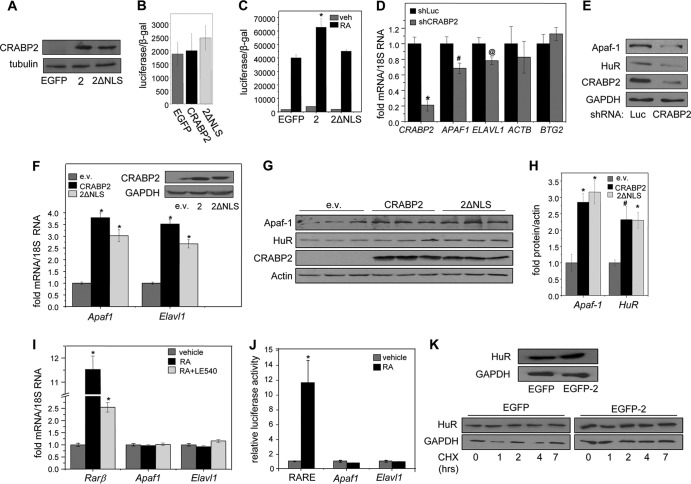
FIG 1.
Apo-CRABP2 upregulates Apaf1 and Elavl1 mRNAs. (A) Immunoblots demonstrating stable overexpression of EGFP-CRABP2 (2) and EGFP-CRABP2ΔNLS (2ΔNLS) in M2−/− cells. (B) M2−/− cell lines stably expressing denoted proteins were cotransfected with a RARE-driven luciferase reporter gene and a vector encoding β-galactosidase. Cells were cultured for 48 h in delipidated media, and luciferase activity was assayed. Data are means ± SDs (n = 3). (C) M2−/− cell lines stably expressing denoted proteins were cotransfected with a RARE-driven luciferase reporter and a vector encoding β-galactosidase. Cells were treated with vehicle or 20 nM RA for 16 h, and luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01 versus RA-treated EGFP-expressing control, determined using two-tailed student t test. (D and E) MCF-7 cells were infected with lentiviruses containing vector harboring shRNA targeting CRABP2 (shCRABP2) or luciferase (shLuc). Three days postinfection, cells were harvested and levels of the indicated mRNAs (D) and proteins (E) were assessed by qPCR and immunoblotting, respectively. *, P ≤ 0.01; #, P = 0.037; @, P = 0.077 (all versus shLuc, determined using two-tailed Student t test). (F) M2−/− cells were transfected with an empty vector (e.v.) or vectors harboring cDNA for CRABP2 or CRABP2ΔNLS. Levels of Apaf1 and Elavl1 mRNAs were measured by qPCR. Data are mean ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01 versus corresponding e.v. control, calculated using a two-tailed Student t test. (Inset) Immunoblots demonstrating CRABP2 expression in M2−/− cells transfected with e.v. or vectors harboring cDNA for indicated proteins. (G and H) M2−/− cells were transfected with e.v. or vectors harboring cDNA for CRABP2 or CRABP2ΔNLS. (G) Levels of Apaf-1 and HuR protein were assessed by immunoblotting. (H) Immunoblots were quantitated; data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01, and #, P = 0.034, both versus corresponding e.v. control and calculated using a two-tailed Student t test. (I) M2−/− cells stably overexpressing EGFP-CRABP2 were treated with RA in the absence or presence of the RAR antagonist LE540 (1 μM each for 4 h). Rarb, Apaf1, and Elavl1 mRNAs were measured by qPCR. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01 versus vehicle control, calculated using a two-tailed student t test. (J) M2−/− cells stably overexpressing EGFP-CRABP2 were transfected with luciferase reporter constructs driven by 2 kb of the proximal promoters of Apaf1 or Elavl1 or by an RARE. Cells were treated with 100 nM RA for 16 h, and luciferase activity was measured. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01 versus corresponding vehicle control, calculated using a two-tailed Student t test. (K) M2−/− cells stably overexpressing EGFP-CRABP2 were treated with 10 μg/ml of cycloheximide for the indicated times. The level of HuR protein was assessed by immunoblotting. (Top) Immunoblot showing HuR protein expression levels in M2−/− cell lines stably overexpressing CRABP2; (bottom) immunoblot showing HuR protein levels after treatment with cycloheximide.