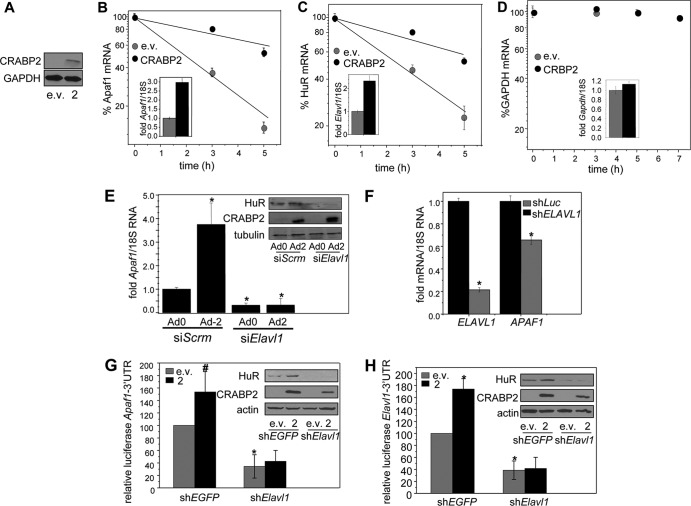
FIG 2.
HuR mediates the ability of CRABP2 to stabilize Apaf1 and Elavl1 mRNAs. (A) Immunoblot demonstrating overexpression of CRABP2. (B to D) M2−/− cells were transfected with e.v. or vector encoding CRABP2 and treated with actinomycin D (2.5 μg/ml). Levels of Apaf1 (B), Elavl1 (C), and Gapdh (D) mRNAs at various time points following treatment were measured by qPCR. Data were normalized to corresponding values at time zero. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). (Inset) mRNA levels of Apaf1, Elavl1, and Gapdh mRNAs in the absence and presence of CRABP2 overexpression at time zero. (E) M2−/− cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siScrm) or siRNA targeting Elavl1 (siElavl1). Twenty-four hours later, cells were infected with control adenovirus (Ad0) or adenovirus encoding CRABP2 (Ad2). Forty-eight hours postinfection, Apaf1 mRNA levels were assessed by qPCR. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P < 0.01 versus cells expressing siScrm and Ad0 by two-tailed Student t test. (Inset) Immunoblots demonstrating decreased expression of HuR in cells expressing siElavl1 and increased expression of CRABP2 upon infection with Ad2. (F) MCF-7 cells were infected with lentiviruses containing vector harboring shRNA targeting ELAVL1 (shELAVL1) or luciferase (shLuc). Three days postinfection, cells were harvested and levels of indicated mRNAs were assessed by qPCR. *, P ≤ 0.01 versus shLuc by two-tailed Student t test. (G and H) M2−/− cells were infected with lentiviruses containing vector harboring shRNAs targeting Elavl1 (shElavl1) or EGFP (shEGFP) and transfected with e.v. or a vector encoding CRABP2 and luciferase reporter harboring the Apaf1 (G) or Elavl1 (H) 3′ UTR. β-Galactosidase was used as a transfection control. Data were normalized to corresponding e.v./shEGFP-expressing cells. Data are means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.01, and #, P = 0.045, both versus e.v./shEGFP control by two-tailed Student t test. (Inset) Immunoblots demonstrating reduced expression of HuR and overexpression of CRABP2.