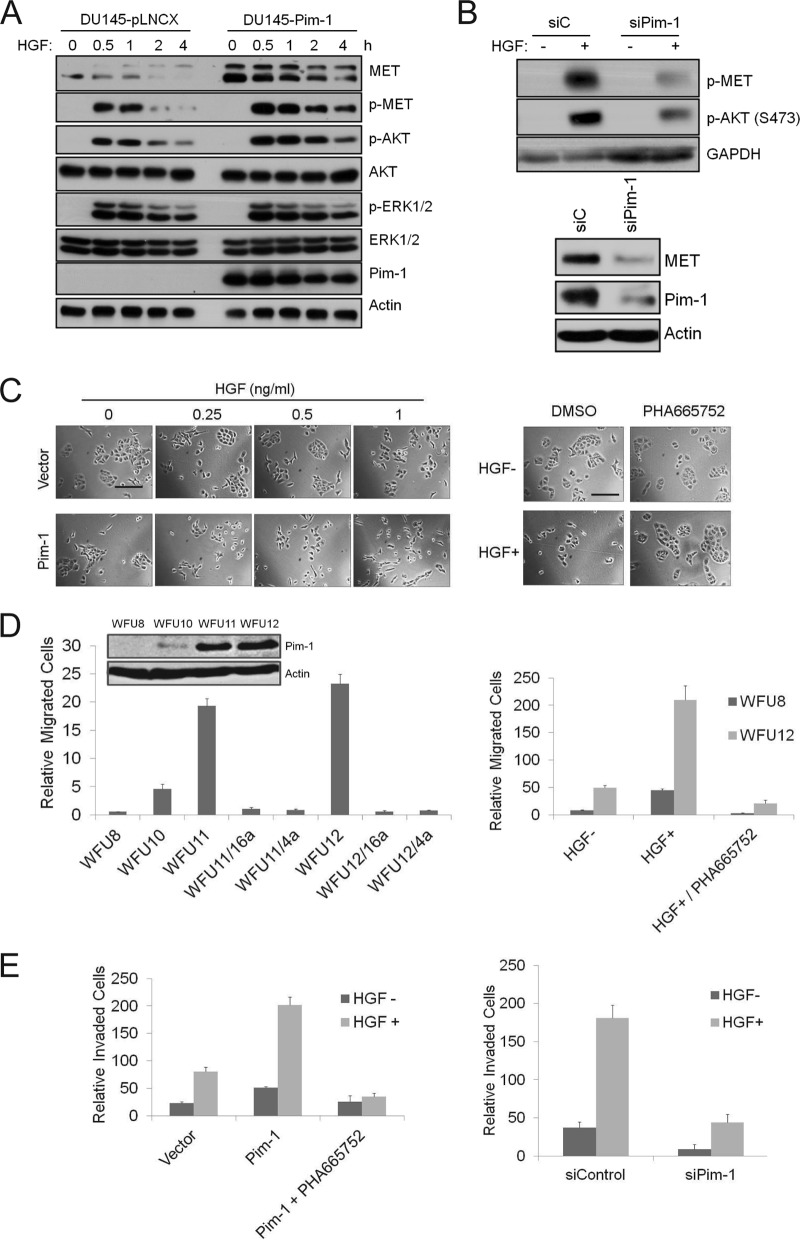
FIG 2.
Pim-1 regulates HGF-MET signaling and cell motility. (A) DU145 cells expressing an empty vector or Pim-1 were serum starved for 24 h before treatment with 100 ng/ml HGF for indicated times. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot assays using the indicated antibodies. (B) (Top) PC3-LN4 cells were transfected with Pim-1 siRNA or a control siRNA for 48 h. Cells were serum starved for 24 h before treatment with 100 ng/ml HGF for 30 min. (Bottom) PC3-LN4 cells were transfected with Pim-1 siRNA or a control siRNA for 72 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot assays using indicated antibodies. (C) (Left) DU145 cells as described for panel A were treated with increasing concentrations of HGF for 24 h. (Right) DU145 cells expressing Pim-1 were treated with 0.25 ng/ml of HGF for 24 h in the presence of PHA665752 (1 μM) or DMSO. Microphotographs show cell scattering effect. Bars, 100 μm. (D) Immunoblots of mouse prostate epithelial cells transduced with a control vector (WFU8) or a Pim-1-expressing construct (WFU10, WFU11, and WFU12) are shown. The migration of these cells was examined for HGF-induced migration over 24 h. HGF (100 ng/ml) was added to the lower chamber. SMI-4a (10 μM), SMI-16a (10 μM), or PHA665752 (1 μM) was added to the upper chamber. Cells migrating through the membrane were counted, and the average ± SD is shown. (E) The invasion of PC3-LN4 cells was assayed using a chamber coated with Matrigel. HGF (100 ng/ml) was added to the lower chamber, and in specific experiments, PHA665752 (1 μM) was added to the upper chamber. Cells were transfected with a Pim-1-expressing plasmid (left) or Pim-1 siRNA (right) for 48 h prior to HGF addition. The average ± SD is shown.