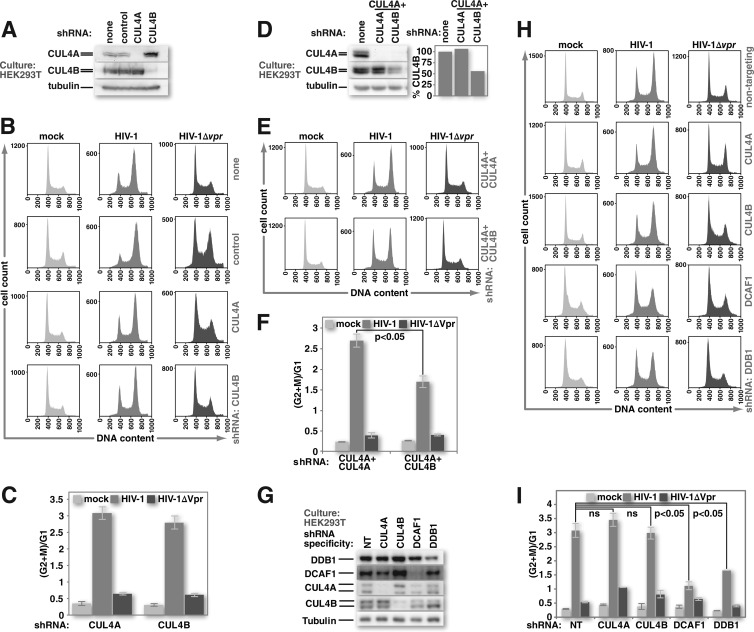
FIG 1.
HIV-1 Vpr can trigger G2 cell cycle arrest in the absence of either CUL4A or CUL4B but not both. (A) Cultures of HEK293T cells or HEK293T cells that stably express shRNA against firefly luciferase (control), CUL4A, or CUL4B were tested for CUL4-specific protein depletion by Western blotting. (B) HEK293T and HEK293T stably shRNA-expressing cell lines were mock infected or infected with HIV-1 or HIV-1 lacking Vpr at equivalent MOIs. Forty-eight hours after infection, cell nuclei were harvested, treated with RNase A and propidium iodide, and analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry. (C) The ratio of nuclei with 4N DNA content (G2+M) to those with 2N DNA content (G1) was determined by using FlowJo software for replicates of the experiment shown in panel B. (D) HEK293T cells that stably express CUL4A-specific shRNA were depleted of CUL4B by transduction of a CUL4B-specific lentiviral expression vector. Transduction with a vector for CUL4A-specific shRNA was used as a control. Cultures under each experimental condition were tested for specific CUL4 protein depletion by Western blotting. (E) The HEK293T cultures described above for panel D were either mock infected or infected with HIV-1 or HIV-1 lacking Vpr. Nuclei from these cells were harvested 48 h after infection and analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry, as described above for panel B. (F) The ratio of nuclei from HEK293T cells, as described above for panels D and E, with 4N DNA content to those with 2N DNA content was calculated and graphed as described above for panel C. (G) HEK293T cells with stably integrated lentiviral vectors that encode doxycycline-inducible shRNAs specific for CRL4 components were induced to express their respective shRNAs for 5 days. Transient depletion of target proteins was confirmed by Western blotting. Expression of a nontargeting (NT) shRNA served as a control. (H) HEK293T cells, as described above for panel G, were either mock infected or infected with HIV-1 or HIV-1 lacking Vpr. Forty-eight hours after infection, nuclei were isolated from these cells, and DNA content was assessed by using flow cytometry as described above for panels B and E. (I) The ratios of 4N to 2N DNA-containing nuclei, from the experiments described above for panels G and H, were calculated and graphed as described above for panels C and F (n = 3). All error bars show standard deviations. The two-tailed Student t test was used to determine statistical significance.