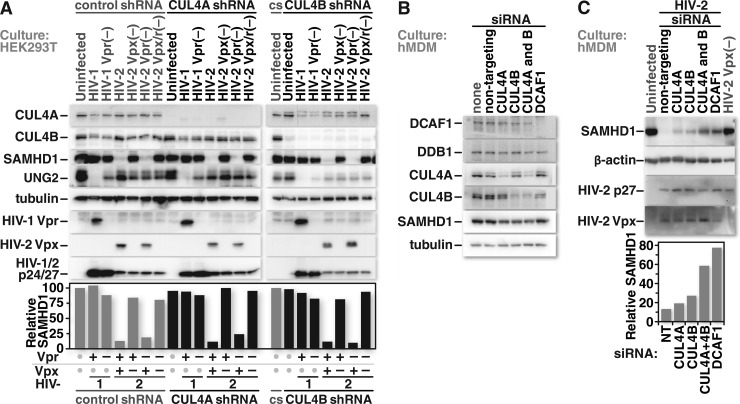
FIG 6.
Vpx can initiate SAMHD1 depletion through either CUL4A- or CUL4B-containing CRL4 complexes, but both CUL4 types are required for maximal SAMHD1 depletion in primary macrophages. (A) HEK293T cells that stably express a control shRNA or shRNAs specific for CUL4A or CUL4B mRNAs were either mock infected or infected at equivalent MOIs with HIV-1, HIV-1 lacking Vpr, HIV-2, or HIV-2 lacking Vpr, Vpx, or both. Twenty-four hours after infection, the cells were collected and lysed. Proteins from the whole-cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and identified by Western blotting using protein-specific antibodies. (B) Cultures of primary human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs) were either mock transfected or transfected with nontargeting siRNA or siRNA specific for the mRNA of the CRL4 complex components indicated. Protein depletion was confirmed by Western blotting. (C, top) Forty-eight hours after siRNA transfection, the cells were either mock infected or infected at a high MOI (MOI = 10) with HIV-2 or HIV-2 lacking Vpx. Less than 24 h after infection, the cells were harvested and lysed. Proteins from whole-cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and identified by Western blotting with protein-specific antibodies. (Bottom) Densitometric measurements performed on the SAMHD1 bands were normalized to the values of the respective β-actin bands. The relative intensities of the SAMHD1 bands were graphed based on the values obtained from the densitometric analysis. Data shown are representative of a trend observed for samples from 3 different donors.