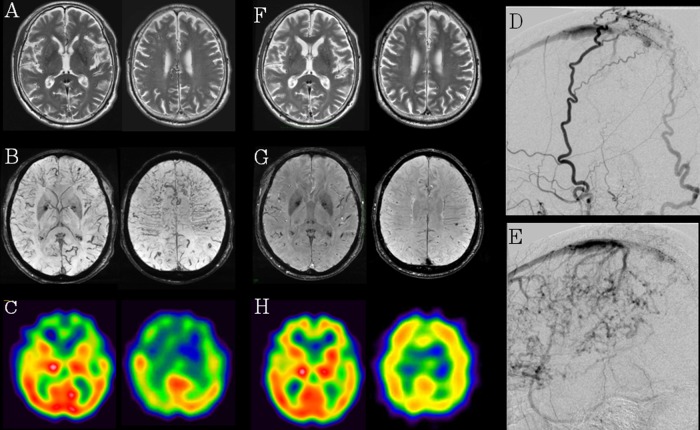
Figure 1.
(A–C) (Pre-embolisation therapy): T2-weighted MRI revealed the slight degree of dilation of the medullary vein in the bilateral frontal and parietal lobes (A). Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) showed marked dilation of the medullary vein in the bilateral frontal and parietal lobes (B). IMP-SPECT of the brain showed hypoperfusion in the frontal lobes bilaterally at rest (C). (D and E) (Selective cerebral angiography): cerebral angiography revealed dural arteriovenous fistula in superior sagittal sinus with cortical venous reflux (D) fed by the superficial temporal artery and occipital artery (E). (F–H) (postembolisation therapy): T2-weighted image (F) and SWI (G) revealed decreased dilation of the medullary vein in the bilateral frontal and parietal lobes and IMP-SPECT showed improved regional cerebral blood flow in the frontal lobes bilaterally (H).