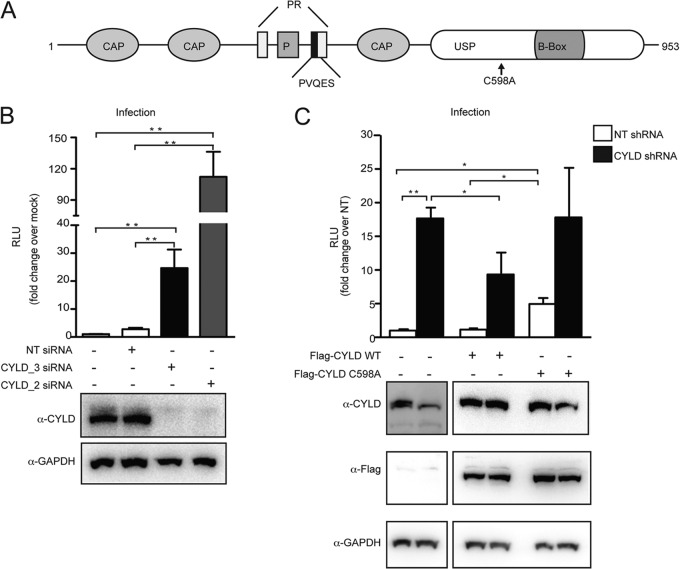
FIG 1.
CYLD silencing increases HIV infection in single-cycle assays. (A) Domain organization of CYLD (isoform 2), showing the cytoskeleton-associated protein domain (CAP), phosphorylation region (P), proline rich region (PR), and ubiquitin-specific protease domain (USP). (B) HEK 293T cells transfected with CYLD-targeting siRNA (CYLD_2 or CYLD_3) or nontargeting siRNA or mock transfected were infected with VSV-G HIV NL4.3 luciferase reporter virus. Relative light units (RLU) were measured after 2 days. Values represent means plus standard errors of the means (SEM) for five independent experiments. Mock is set at 1, and values represent fold changes over mock. The average RLU for the mock control was 5,732 ± 3,300. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (unpaired t tests, Prism software). Knockdown efficiency was quantified by immunoblotting using an antibody against endogenous CYLD and an antibody against GAPDH as a loading control (lower panel). (C) HEK 293T cells stably expressing nontargeting shRNA (NT shRNA) or shRNA targeting CYLD (CYLD shRNA) were transfected with empty plasmid, the short-hairpin-resistant form of Flag-CYLD WT, or the short-hairpin-resistant form of the catalytically inactive mutant of Flag-CYLD (C598A). At 1 day posttransfection, cells were infected with VSV-G HIV NL4.3 luciferase reporter virus (upper panel). Luciferase (relative light units [RLU]) was measured 2 days postinfection. Values represent means plus SEM for three independent experiments. The NT shRNA transfected with an empty vector was set to 1, and values represent fold changes over NT shRNA-expressing cells. The average RLU for the mock control was 1,148 ± 1,093. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (unpaired t tests, Prism software). Expression of endogenous or FLAG-tagged CYLD was analyzed by Western blotting (lower panel). GAPDH expression served as loading control.