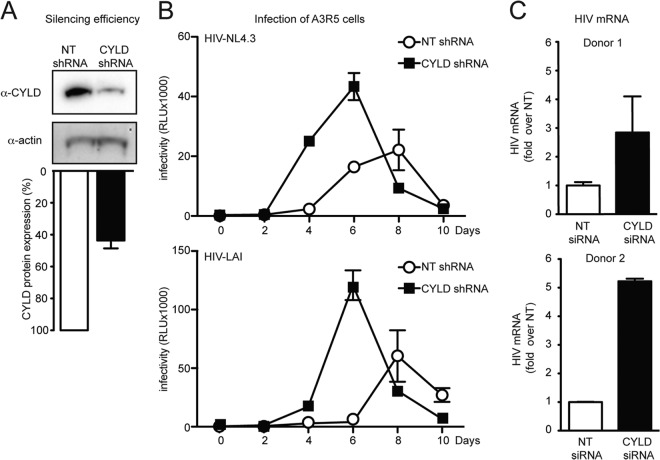
FIG 6.
HIV transcription increases upon CYLD knockdown in immortalized and primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. (A) Efficiency of CYLD silencing. A3R5 T cell CYLD shRNA and NT shRNA were determined by Western blot analysis (upper panel) and quantified by densitometric analysis (lower panel). (B) A3R5 T cell CYLD shRNA and NT shRNA were infected with the indicated viruses. Clarified supernatants were collected every 2 days, and infectivity was determined by a TZM-bl infectivity assay. (C) Primary CD4+ T cells from two healthy donors were stimulated for 48 h with IL-2/PHA and transfected with CYLD siRNA and nontargeting siRNA (NT siRNA, control). At 48 h posttransfection, CD4+ T cells were infected with VSV-G-pseudotyped NL4.3/Env− HIV, and expression of HIV mRNA was measured at 24 h postinfection by qPCR. The HIV mRNA expression in NT siRNA is set at 1, and values represent fold induction over NT shRNA. Error bars represent standard deviations for duplicate qPCR analysis. Expression of HIV mRNA relative to the housekeeping gene rsp11 was 0.016 for donor 1 and 0.8 for donor 2. CYLD silencing efficiency was around 60% for both donors as determined by qPCR analysis.