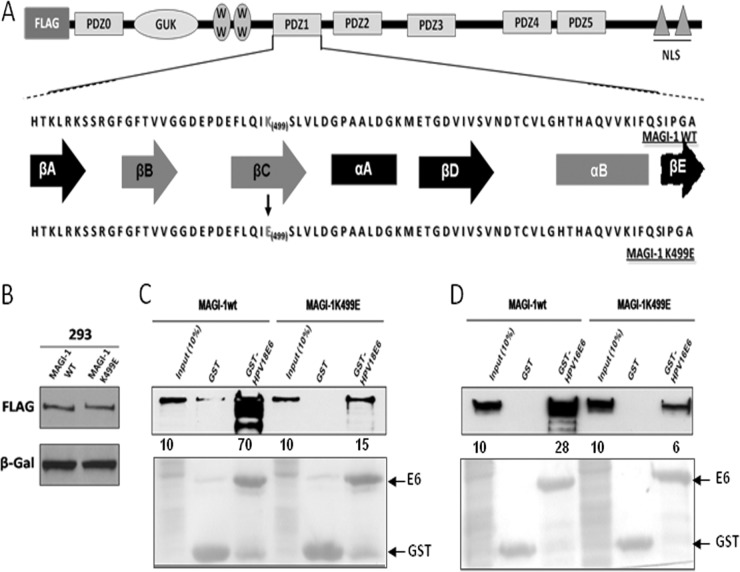
FIG 1.
The K499E mutation perturbs E6 interaction with MAGI-1. (A) Diagram showing the domain composition of MAGI-1 and the location of the K499E mutation. Elements of secondary structure that compose the PDZ1 are also shown (βA to βE, β-strands A to E; αA and αB, α-helix A and B), and those involved in the interaction with E6 and other target proteins are highlighted in red (adapted from Fournane et al. [32]). (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with 1 μg of FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant MAGI-1 expression plasmids and grown for 24 h prior to harvesting. The levels of MAGI-1 expression were assessed by Western blotting. β-Galactosidase was included to monitor the transfection efficiency. (C and D) Extracts from HEK293 cells transfected with 3 μg of wild-type or mutant MAGI-1 expression plasmids were subjected to GST-pulldown assays with the indicated GST fusion proteins, and bound MAGI-1 was detected by Western blotting using anti-FLAG antibody. Numbers represent the percentage of wild-type and mutant MAGI-1 proteins bound to the indicated GST fusion protein relative to the input control. The lower panel shows the Ponceau staining of the membrane, confirming the equal loading of GST proteins.