FIG 13.
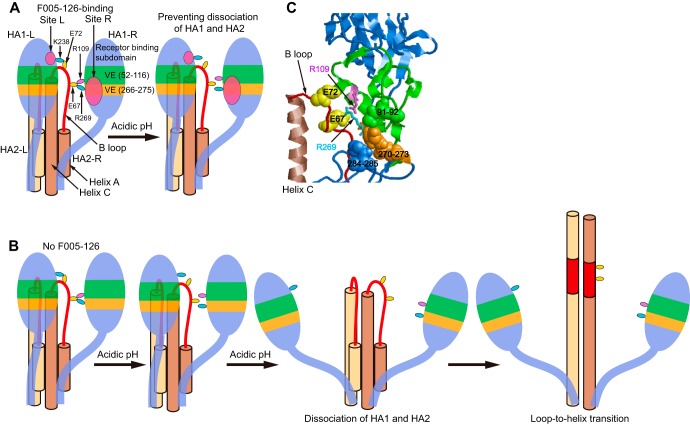
Illustrations on a proposed mechanism for preventing dissociation of HA1 and HA2 by F005-126. (A and B) HA1, helix A, B loop and helix C in two HA protomers in an HA trimer are illustrated. A vestigial esterase (VE) subdomain is green (residues 52 to 116) and orange (residues 266 to 275), and other regions in HA1 are blue. Arg109 and Arg269 are violet and cyan, respectively. Glu67 and Glu72 in B loop are yellow. Sites L and R are indicated in magenta. Under the low-pH condition, initially, part of the salt bridges are broken, and finally, the salt bridges are completely broken. When F005-126 binds to HA, dissociation does not occur at low pH, even if the salt bridges are broken (A). Dissociation of HA1 and HA2 occurs at low pH without F005-126 (B). (C) Arg109 and Arg269 are depicted as sticks in violet and cyan, respectively. Glu67 and Glu72 in B loop are depicted as surface representation in yellow. Residues 91, 92, 270 to 273, 284, and 285 in site R are depicted as surface representations.