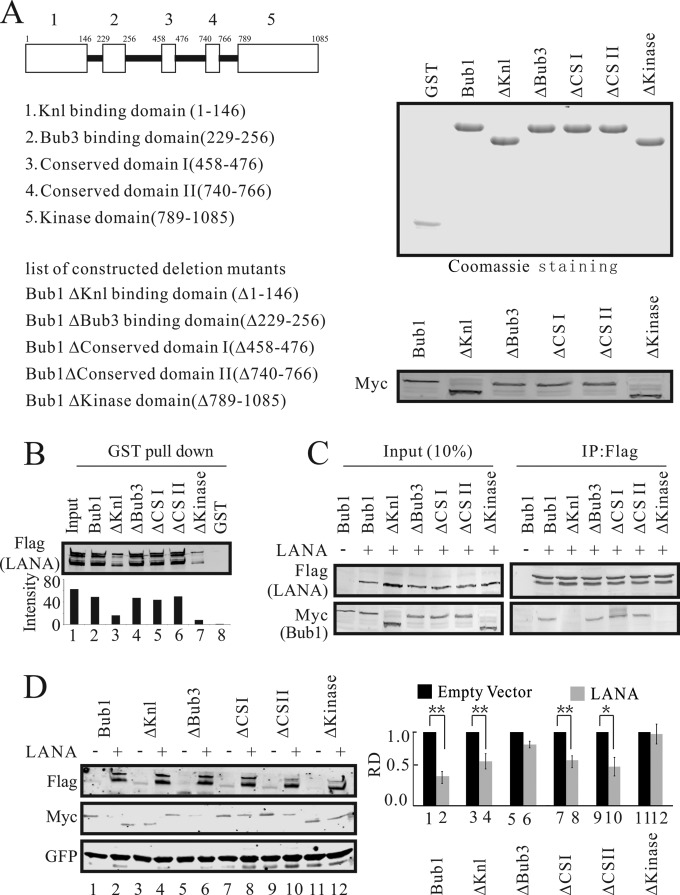
FIG 2.
The Knl and kinase domains of Bub1 are necessary for its interaction with LANA. (A) (Left) Schematic diagram of Bub1 mutants. (Right) (Top) GST-tagged proteins purified from Escherichia coli. (Bottom) Eukaryotic expression of these deletion mutants (Myc tagged). ΔCSI and ΔCSII, Bub1 mutants with deletions of conserved domain I and conserved domain II, respectively. (B) Beads coated with GST or with fusion proteins consisting of GST and Bub1 domain deletion mutant proteins were incubated with lysates from HEK-293 cells electroporated with pA3F-LANA for GST pulldown assays. The pulldown of LANA was detected by Western blotting using antibody M2. (C) Bub1 interacts with LANA through its kinase and Knl binding domains. HEK-293 cells were electroporated with pA3F-LANA and pA3M-Bub1 or its related domain deletion mutants. Forty-eight hours after electroporation, the cell lysates were prepared for IP with antibody M2 and Western blotting with antibodies 9E10 and M2. (D) HEK-293 cells were electroporated with pA3F-LANA, pA3M-Bub1 or its related domain deletion mutants, and GFP. Forty-eight hours later, cells were collected for Western blot analysis. GFP served as a control for protein loading. The relative densities (RD) of Bub1 and its related deletion mutants were quantified and plotted against the signal obtained from the control after normalization to GFP. Statistical significance was evaluated by using P values of <0.05 (*) and <0.01 (**).