Figure 1. macroH2A chromatin deposition increases upon differentiation and is lost upon reprogramming.
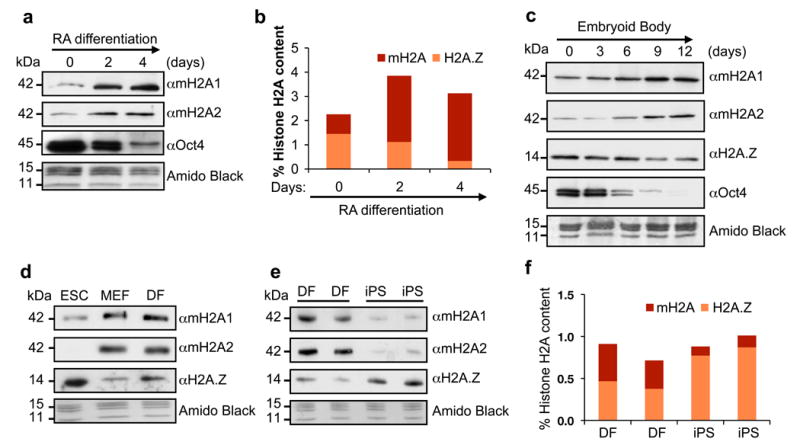
(a) Acid extracted histones from RA-differentiated CCE ESCs probed for macroH2A isoforms. Chromatin-bound Oct4 is used to confirm differentiation; Amido Black of core histones used for loading. (b) Histone H2A variant composition as analyzed by qMS during ESC RA-induced differentiation. Values represented as percentage of total H2A; two biological replicates, 6 technical replicates shown. (c) Chromatin fraction of EB time course (E14 ESCs) used to probe H2A variants. Oct4 is used to confirm differentiation; Amido Black of core histones used for loading. (d) Chromatin fraction of CCE ESC, MEFs and DFs probed for H2A variants. (e) Wt mouse DFs and their iPS-reprogrammed counterparts probed for H2A variants. (f) qMS analysis of macroH2A and H2A.Z using histones isolated from cells used in (e).
