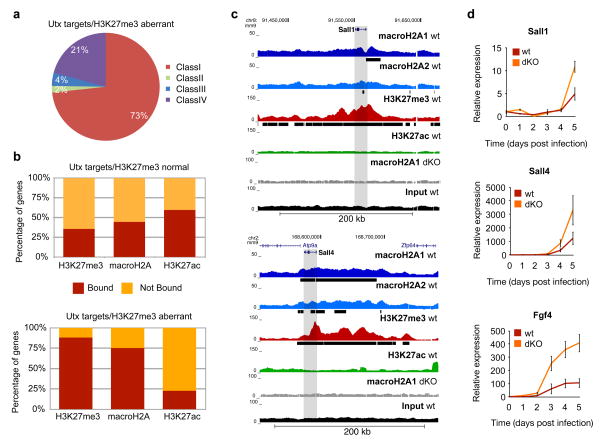
Figure 5. macroH2A occupancy inhibits activation of Utx target genes required early in iPS reprogramming.
(a) Pie chart of Utx target genes with aberrant H3K27me3 methylation (in Utx KO)33 composed of the four classes of genes from Fig. 4c. (b) Comparison of genes marked by H3K27me3, H3K27ac and macroH2A-bound genes (combined macroH2A1 and macroH2A2 targets) in wt DFs and genes reactivated early in iPS reprogramming with normal H3K27me3 demethylation in Utx KO cells (top) versus genes that aberrantly retain H3K27me3 in Utx KO cells (bottom)35. MacroH2A is enriched in genes that are unable to demethylate H3K27me3 in the absence of Utx. (c) ChIP-seq profile (UCSC browser) of two genes bound by macroH2A1, macroH2A2 and H3K27me3 in DFs that are not properly demethylated in the absence of Utx during reprogramming (Sall1 and Sall4 - grey bar represents the gene body region). Chromatin ‘domains’ identified with Sicer annotated under each profile (black bar). MacroH2A1 ChIP-seq in dKO DFs and Input used as controls. (d) Time course analysis of mRNA expression of three Utx target genes (Fgf4, Sall1 and Sall4) during reprogramming shows delayed induction in wild type DFs as compared to macroH2A dKO DFs. Relative expression is plotted using ribosomal L7 as a house keeping gene, and compared to DFs at day 0, mean ± s.d. (n=3).